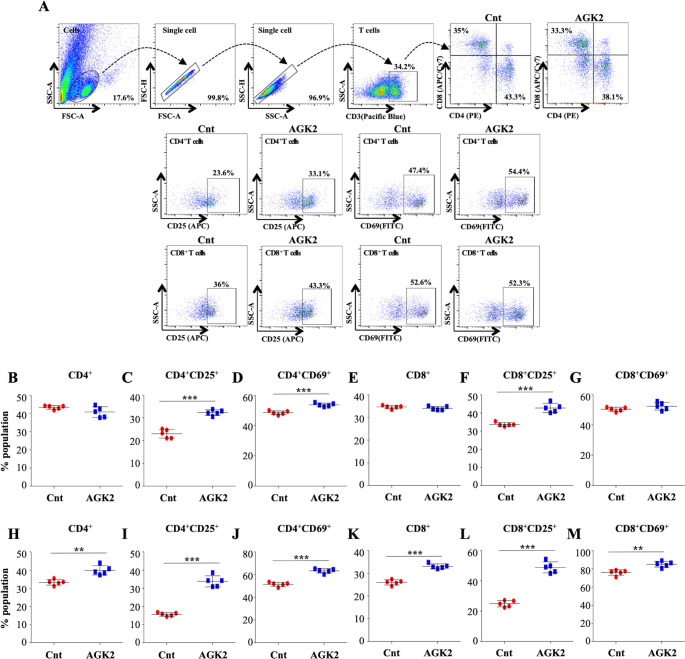
Figure 8. SIRT2 inhibition ameliorates T cell activation in the lungs and spleen of infected mice.
Cells isolated from the lungs of control and AGK2-treated Mtb-infected C57BL/6 animals were subjected to surface staining (CD3-Pacific Blue, CD4-PE, CD8-APC/Cy7, CD69-FITC and CD25-APC) followed by FACS analysis. (A) Gating strategy and representative dot plots. Scatter plots depicting the percentage of CD4+, CD4+CD69+, CD4+CD25+, CD8+, CD8+CD69+ and CD8+CD25+ T cells in the (B–G) lungs and the (H–M) spleen of infected mice. The experiment was performed twice with five mice in each group. Data is represented as mean ± SD (n = 5). **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005.