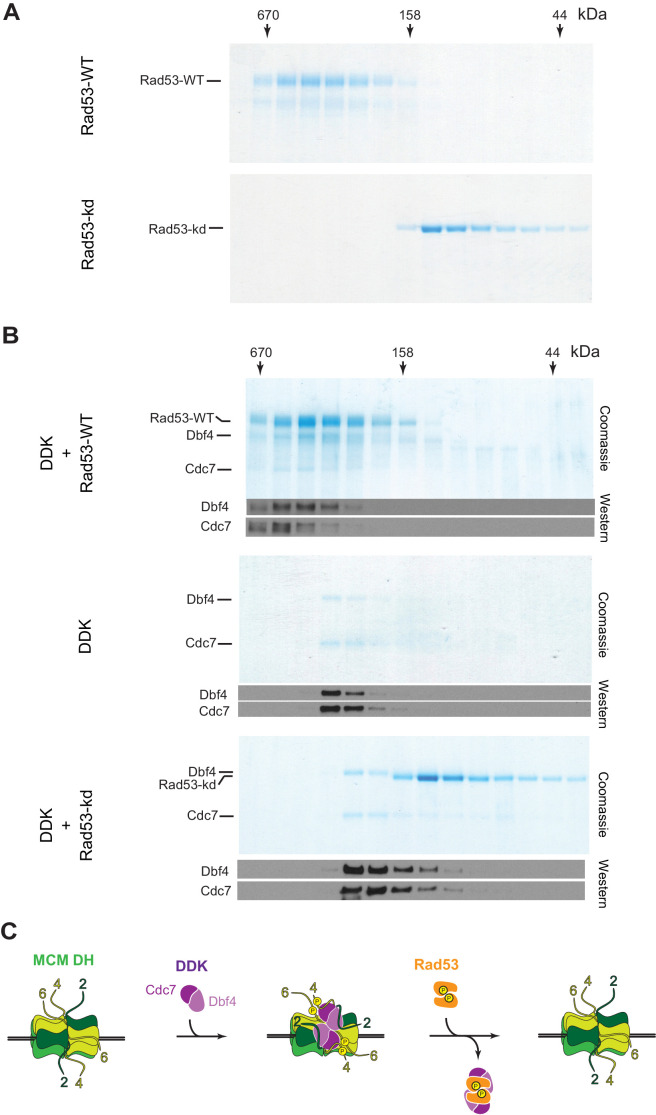
Figure 7. Rad53-WT, but not Rad53-kd, can form a stable complex with DDK.
(A) Gel-filtration analysis of purified Rad53-WT (top) or Rad53-kd (bottom), as indicated. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stain. (B) Gel-filtration analysis of Rad53-WT + DDK (top), DDK alone (center), or Rad53-kd + DDK (bottom). Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stain or western blot, as indicated. (C) Model illustrating the inhibition of DDK-MCM DH complex formation by competitive binding of activated Rad53 to DDK.