Fig. 1. Structure of hyaluronic acid.
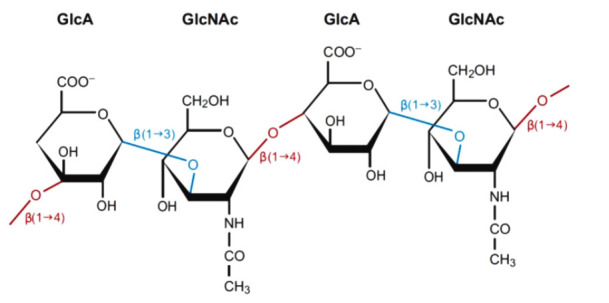
D-Glucuronic acid and D-N-acetylglucosamine are linked by β-1,3 bonds (blue) to form a disaccharide. Multiple disaccharides are linked by β-1,4 bonds (red) to form hyaluronic acid. Mammalian and microbial hyaluronidases cleave β-1,4 bonds (red), and leech/hookworm hyaluronidases degrade β-1,3 bonds (blue).
