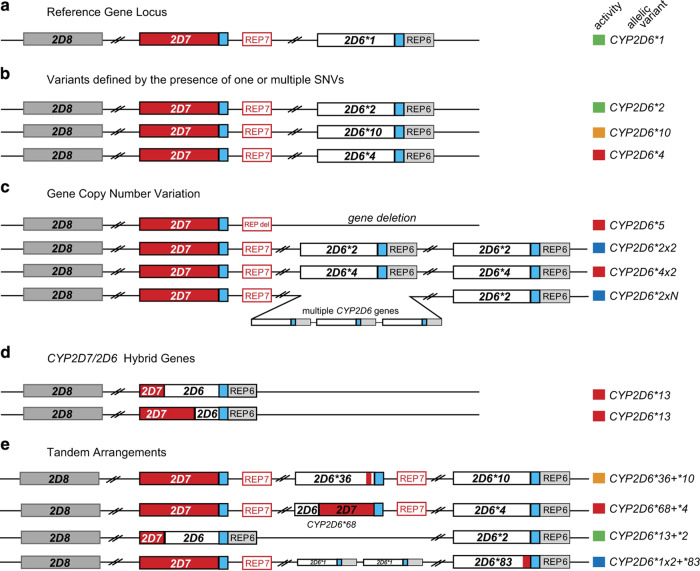
Fig. 1. Graphical overview of the highly polymorphic CYP2D6/2D7/2D8 locus, by Twist et al.15, licensed under Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). No changes have been made to the figure content.
a The relative position of the reference CYP2D6*1 haplotype (white) to two non-functional paralogs, CYP2D7 (red) and CYP2D8 (grey) on the minus strand of Chromosome 22. REP6 and REP7 are paralogous, Alu-containing, 600-bp repetitive sequences found downstream of CYP2D6 and CYP2D7, respectively. The blue boxes indicate identical unique sequences downstream of CYP2D6 and CYP2D7. Notice the “spacer” (1.6-kb) separating REP7 from CYP2D7 but none between CYP2D6 and REP6. b Common CYP2D6 star alleles defined by core single nucleotide variants (SNVs). c Examples of CYP2D6 copy number variations and their functional annotation. d Examples of CYP2D7/2D6 hybrid genes. e Common tandem rearrangements in the CYP2D gene locus. The activity level boxes on the right are coded; red for a non-functional haplotype, orange for decreased activity, green for fully functional reference activity, and blue for increased activity.