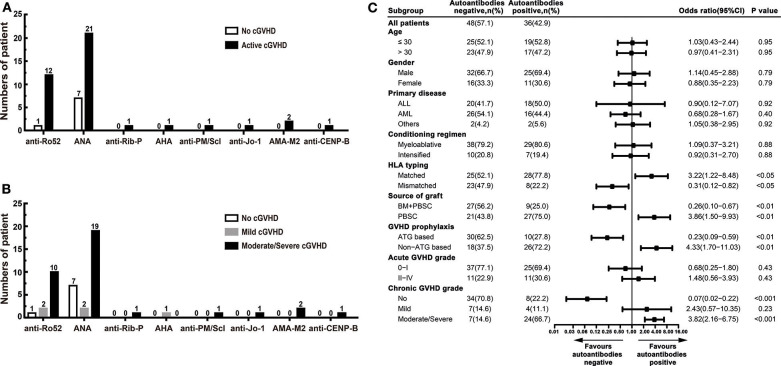
Figure 1.
The prevalence of autoantibodies in patients after allo-HSCT. (A) The numbers of positive autoantibodies in patients without cGVHD and patients with active cGVHD. (B) The numbers of positive autoantibodies in patients with different severities of cGVHD. (C) Stratified analysis for factors associated with the presence of autoantibodies. The black bars in the forest plot indicate odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals for each variable. cGVHD, chronic graft-vs.-host disease; anti-Ro52, anti-Ro52 autoantibodies; ANA, anti-nuclear autoantibodies; anti-Rib-P, anti-ribosomal P protein autoantibodies; AHA, anti-histone autoantibodies; anti-PM/Scl, anti-polymyositis/scleroderma autoantibodies; anti-Jo-1, anti-histidyl tRNA synthetase autoantibodies; AMAM-2, anti-mitochondrial autoantibodies type 2; anti-CENP-B, anti-centromere-B autoantibodies; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; BM, bone marrow; PBSC, peripheral blood stem cell; ATG, antithymocyte globulin.