Fig. 2.
The clinical responses before and after ssCART-19 infusions in patients.
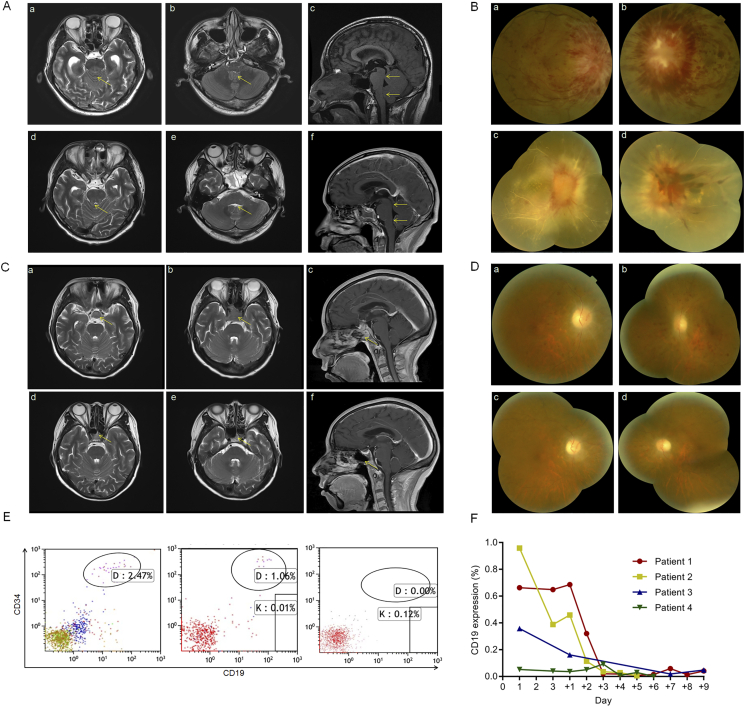
A (a) The T2-Weighted imaging (T2WI) signal of the pontine parenchyma in patient 1 was slightly high (arrowhead). (b–c) The end of the central aqueduct and four ventricle outlets became narrow (arrows), secondary to mild obstructive hydrocephalus. (d–f) One month after treatment, the pontine dorsal swelling in patient 1 was significantly reduced, the T2WI signal was nearly normal, and the degree of stenosis decreased at the end of the central aqueduct and at the outlet of the fourth ventricle.
B (a–b) The fundus showed papillary edema and a flame-shaped hemorrhage on the surface of the optic disc and nearby retina. The height of the optic disc was over the scale of optical coherence tomography (OCT). These photos were taken when patient 1 was admitted. (c–d) The optic disc edema subsided, the hemorrhage was absorbed in the right eye, and all the vessels of the retina became white-line-like. Bleeding clots in the left eye covered the optic disc. These photos were taken one month after infusion in patient 1.
C (a–c) T2WI signals showed pituitary tumors in the sellar region (arrows) when patient 3 was enrolled. (d–f) Tumors were significantly reduced and almost disappeared on day +35 after CAR-T therapy (arrows).
D (a–b) The optic disc showed edema and was pale. A large amount of punctate bleeding was observed on the retina. These photos were taken when patient 2 was admitted. (c–d) The optic disc edema was alleviated, and the bleeding decreased. These photos were taken one week after infusion in patient 2.
E MRD of ALL was evaluated in CSF in patient 3 by flow cytometric analysis on days −5, +1 and +7.
F Flow cytometry analysis of PB from patients after CAR-T infusion using antibodies against CD3 and CD19.