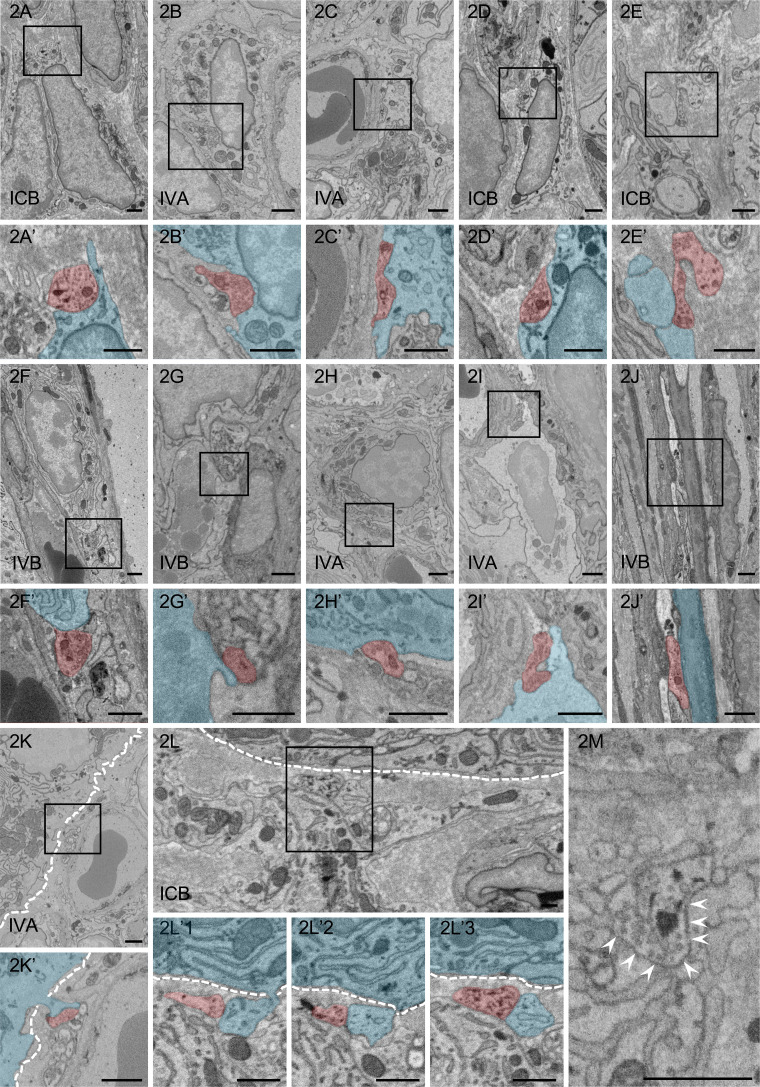
Fig. 2.
Ultrastructural observation of contacts between nerve fibers (red) and target cells (blue). A–L: Nerve fibers are in contact with the type II fibroblast-like cell (FBLC) (A), the type III FBLC (B), the type IV FBLC (C), the macrophage-like cell (MLC) (D), the monocyte-like cell (E), the plasma cell (F), the mast cell (G), the eosinophil (H), the lymphocyte-like cell (I), the villous myocyte (J), the villous columnar epithelial cell (K), and the Paneth cell (L). A’–K’: High-magnification images of the squares in panels A–K, respectively. Synaptic vesicle-like structures are observed in each contact structure. Contact structures against the type II FBLCs (A’), the type III FBLC (B’), the type IV FBLC (C’), the MLC (D’), the monocyte-like cell (E’) the eosinophil (H’) and the lymphocyte-like cell (I’) dig into the cellular bodies of the target cells. L’1–3: Ultrastructural serial images showing the contact between a nerve fiber and a cellular process of the Paneth cell in panel L. L’3: High-magnification image from the square in panel L. The Paneth cell (blue) extends a cellular process penetrating the basal lamina and is in contact with a nerve fiber (red). M: Many synaptic vesicle-like structures are present in the contact structure showing the swelling pattern. A contact site between a nerve fiber and the type IV FBLC is indicated by arrowheads from the side of the type IV FBLC. White dashed line, epithelial basal lamina. IVA, apical portion of the villi. IVB, basal portion of the villi. ICB, basal portion of the crypts. Bar=1 µm.