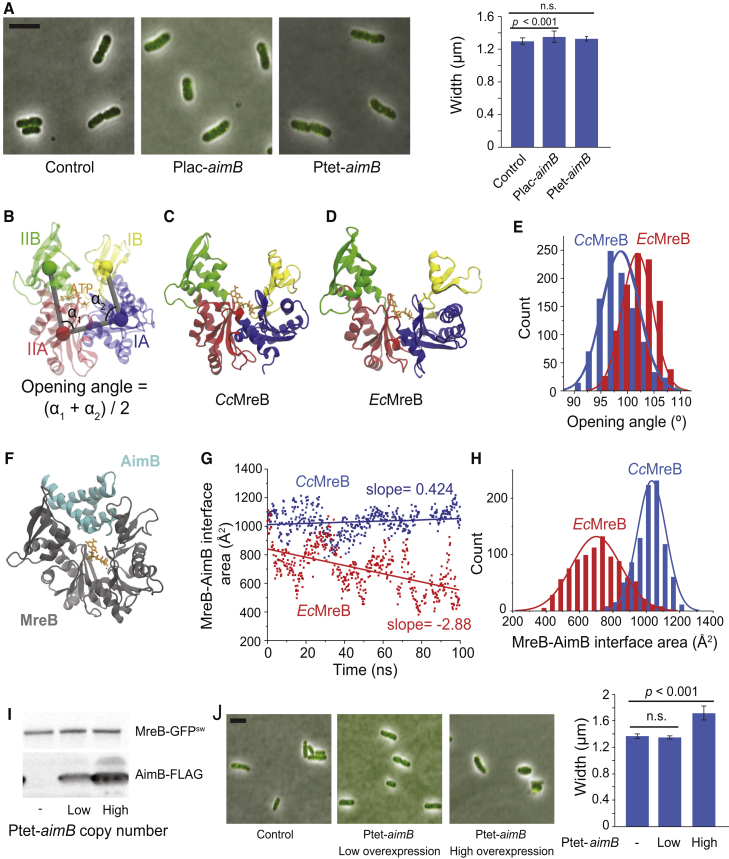
Figure 4.
AimB has low affinity for EcMreB, potentially because of differences in the binding pocket. (A) E. coli expressing MreB-GFPsw were transformed with low-copy plasmids for AimB-FLAG expression and induced with 1 mM IPTG or 100 ng/mL aTc for 6 h. Cells were back diluted 1:500 at 3 h to maintain log-phase growth. Cells were imaged by phase and fluorescence microscopy (overlay on left), and cell widths were analyzed (right). Minimal effects on cell width or shape were observed (n = 139 control, 106 Plac, 150 Ptet; error bars are SD; p-values are two-tailed t-test). Scale bars, 5 μm. (B) Definitions of opening angle for an MreB monomer are shown. The centers of mass of the four subdomains are shown as colored spheres. (C) Snapshot of an ATP-bound CcMreB (PDB: 4CZM) at the end of a 100-ns simulation is shown. (D) Shown is a snapshot of an ATP-bound EcMreB at the end of a 100-ns simulation, demonstrating a larger opening angle than CcMreB in (C). The initial EcMreB structure was a homology model of EcMreB built from the CcMreB crystal structure. (E) EcMreB exhibited larger opening angles than CcMreB in the last 30 ns of MD simulations. (F) Shown is the docking of a homology model of the Jannaschia sp. protein Jann_2546 (PDB: 2KZC), a homolog of AimB, to the equilibrated open structure from a CcMreB MD simulation. (G and H) The interfacial area between MreB and AimB showed that the docked heterodimer of CcMreB and AimB in (F) remained stable throughout 100 ns of MD simulation (Video S1), whereas the interfacial area of AimB docking to EcMreB decreased over time (G, Video S2). The distribution of interfacial areas over the course of the MD simulation demonstrates that AimB interacts more stably with CcMreB (H). (I and J) Substantial overexpression of AimB in E. coli disrupts cell width and MreB localization. EcMreB-GFPsw strains harboring low- or high-copy vectors for AimB-FLAG expression were induced as in (A). In (I), cell lysates (normalized to OD600) were analyzed by immunoblotting. In (J), cellular dimensions were quantified by phase and fluorescence microscopy (n = 30 control, 39 low-copy, 31 high-copy; error bars are SD; p-values are two-tailed t-test). Scale bars, 5 μm. To see this figure in color, go online.