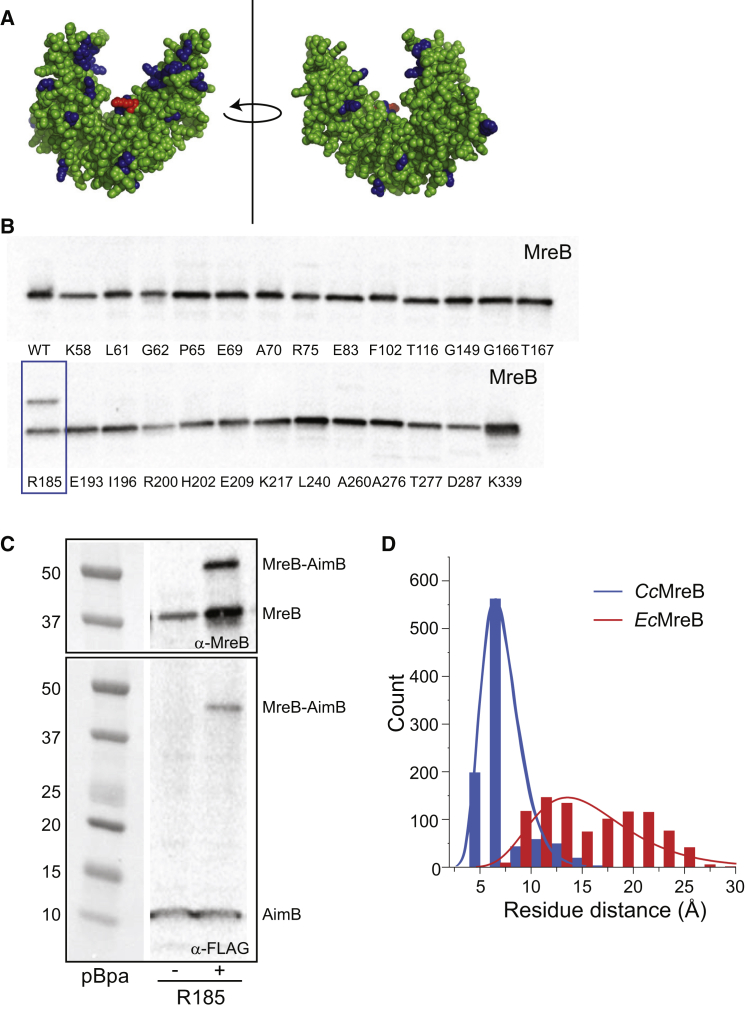
Figure 5.
AimB and MreB interact directly. (A) The location of the 26 residues of MreB that were mutated to the amber codon for in vitro cross-linking assays are highlighted in blue on the CcMreB crystal structure. Arginine 185 is highlighted in red. (B) In vitro cross-linking experiments were performed by incorporating the UV cross-linkable non-natural amino acid pBPA at various positions in MreB (Materials and Methods). Cross-linked samples were analyzed by immunoblotting for MreB. A cross-linked band was observed for position R185 (blue rectangle). (C) UV cross-linking of R185 was performed as in (A) using a FLAG-tagged AimB construct. Immunoblotting for MreB or the FLAG-tagged AimB showed similar cross-linked bands. (D) R185 is at the base of the cleft where AimB and MreB are predicted to interact. The intermolecular distance between MreBR185 and AimBG64, the nearest AimB residue, was quantified over the course of our CcMreB-AimB and EcMreB-AimB MD simulations. AimB interacts with CcMreB more stably compared with EcMreB, as shown by a smaller distance between the two residues. To see this figure in color, go online.