Fig. 6. Nuclear stiffness regulates RhoA activity and cell migration phenotype in confinement.
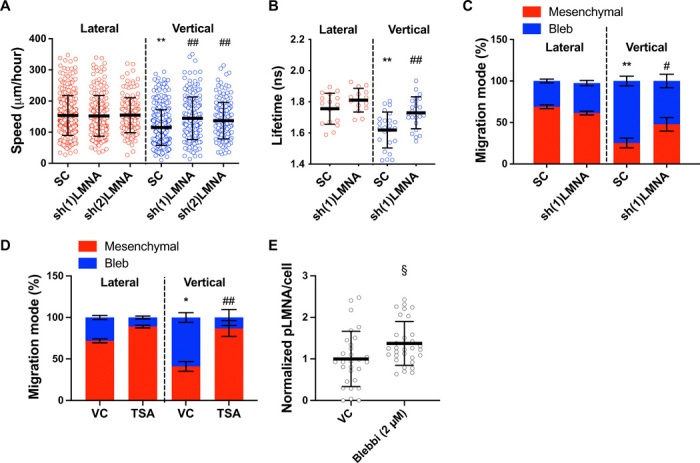
(A) Migration speeds of HT-1080 scramble control and LMNA-KD cells (n ≥ 149; three independent experiments) using two different shRNA sequences. (B) RhoA activity of scramble control and LMNA-KD HT-1080 cells, as measured by FLIM-FRET (n ≥ 14 cells; two or more independent experiments). (C) Migration phenotypes of scramble control and LMNA-KD HT-1080 cells, as assessed after fixing and staining cells with actin phalloidin (n ≥ 3 independent experiments; ≥20 cells per condition). (D) Migration phenotypes of vehicle control and TSA-treated (100 ng/μl) HT-1080 cells, as assessed after fixing and staining cells with actin phalloidin (n ≥ 3 independent experiments; ≥10 cells per condition). (E) Quantification of phosphorylated LMNA (pLMNA) per cell for vehicle control versus blebbistatin-treated (2 μm) cells, as measured from the average intensity projection of cells fixed and stained for pLMNA (n ≥ 29 cells; two independent experiments). Values represent the mean ± SD (A, B, and E) or means ± SEM (C and D). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 relative to lateral control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 relative to vertical control; §P < 0.05 relative to 2D control.
