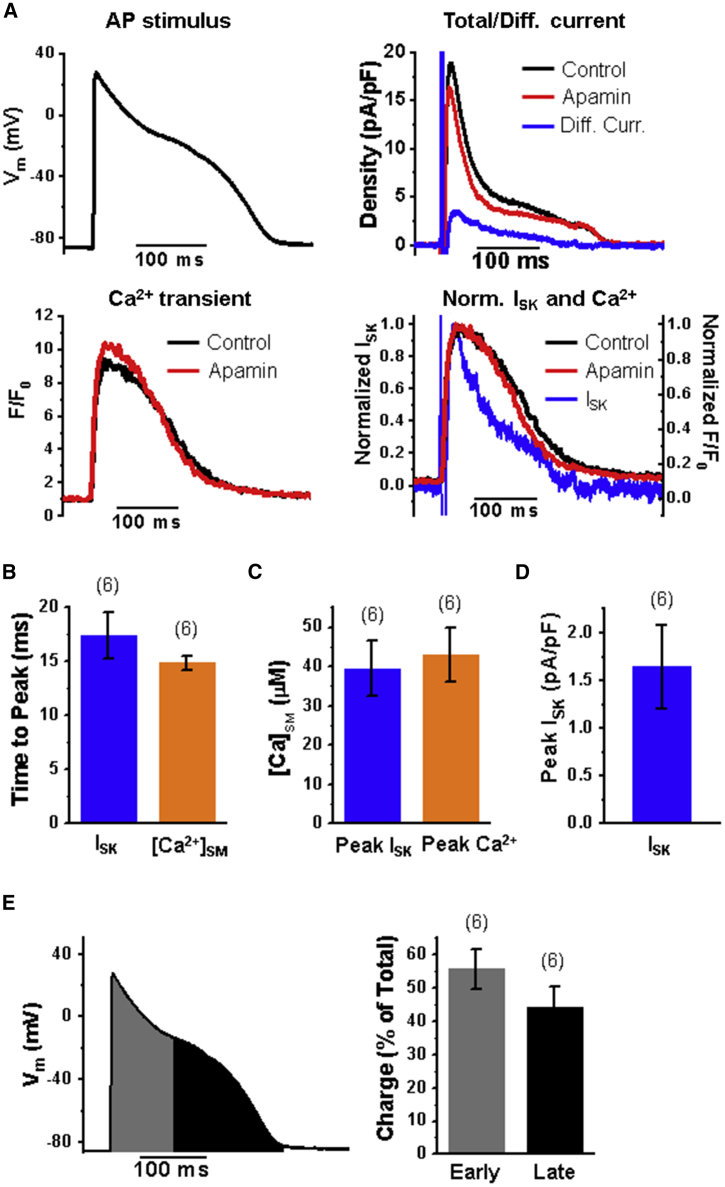
Figure 3.
A significant portion of ISK occurs during later stages of AP. (A) Sample AP clamp traces showing voltage stimulus (left), total current before and after apamin with difference current (black minus red trace, blue), Ca2+ transient before and after apamin (bottom left), and normalized ISK and normalized Ca2+ transient (F/F0) showing the correlation of ISK with Ca2+ transient (bottom right). The Ca2+ transients were compared before and after apamin to find recordings with similar evoked Ca2+ transients to properly isolate the apamin-sensitive current. The corresponding current traces were used to find the difference current. All recordings were obtained in the presence of 100 nM ISO. (B) Time to peak plot for peak ISK and peak submembrane Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]SM) during AP clamp. (C) [Ca2+]SM at peak ISK and peak Ca2+ transient. (D) Mean peak ISK amplitude during AP clamp. (E) Plot of the stimulus voltage showing the division of the AP stimulus into two regions corresponding to early and late stages (left). Plot of percentage of total SK channel charge in the early and late phases of the AP stimulus (right). n = 6; N = 6; mean ± SE for all plots.