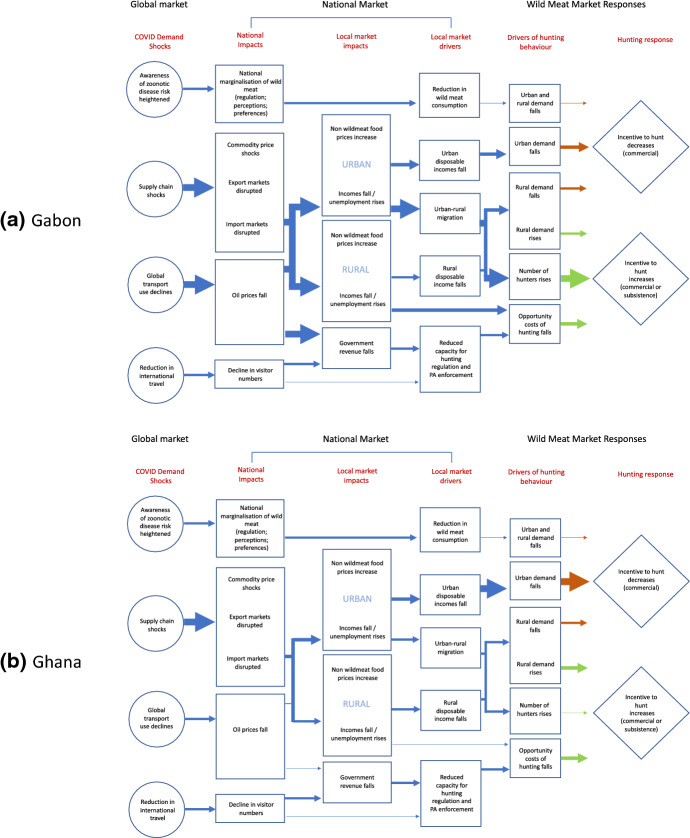
Fig. 2.
Causal flow models showing possible key pathways of action linking select COVID-19 shocks with the wild meat trade. With low dependence on oil and tourism, luxury urban wild meat markets, and depleted wildlife resources Ghana is likely to experience limited, but potential locally acute, additional reliance on wild meat. This may be particularly acute near Protected Areas (denoted PA). By contrast, Gabon’s oil economy, inelastic wild meat demand and abundant wildlife resources may come under increased pressure if substantial economic and logistical shocks persist due to COVID-19, particularly as a result of increased numbers of returnee hunters. This will only be offset to a limited extent by reductions in urban demand as the economy shrinks. Predicted intensity of impact is denoted by line width: 1. Negligible (thin line), 2. Minor 3. Moderate, 4. Strong (thick line)