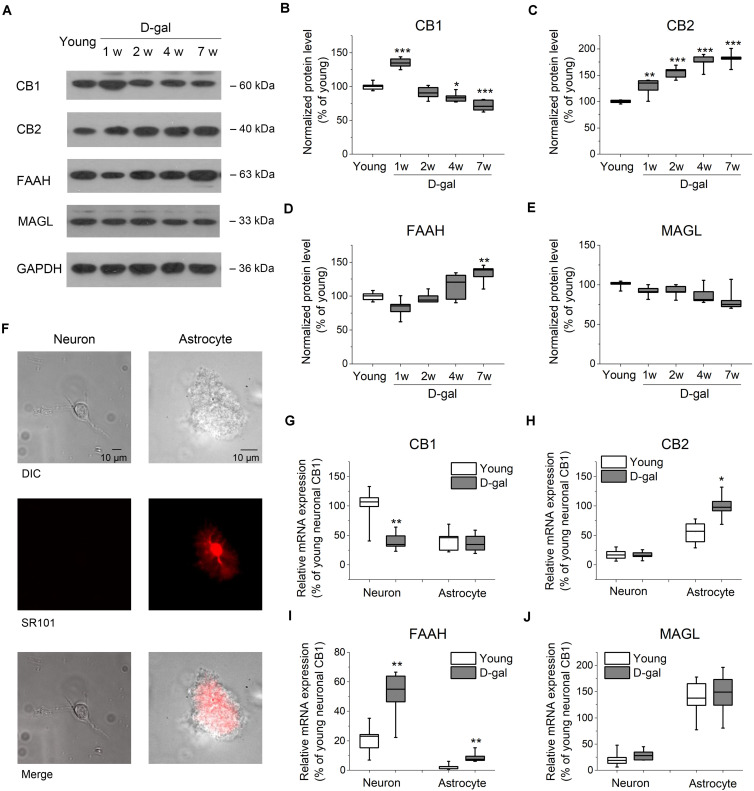
FIGURE 2.
D-gal treatment altered protein and mRNA expression of key ECS components in hippocampus. (A) Western immunoblot analysis of the protein expression of cannabinoid receptor CB1 and CB2, fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) in hippocampus. Protein was analyzed at 1, 2, 4, and 7 weeks (w) after D-gal injection. Rats with a 7-week injection of vehicle (0.9% NaCl) were used as young control. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) Quantification of CB1 protein in hippocampal tissue. The densitometric data are normalized by GAPDH and presented as a percentage of the level of young rats. (C–E) Similar to (B), except that CB2, FAAH, and MAGL were measured in (C–E), respectively. n = 4–5 rats/group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with the young control as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s t-test. (F) Morphology of freshly isolated neuron and astrocyte from rat hippocampus CA1 area. Scale bar: 10 μm. Pyramidal neurons were selected based on their morphology and negative SR101 staining, and astrocytes were chosen based on their positive SR101 staining. These cells were harvested separately for qRT-PCR analysis. (G) Quantification of CB1 mRNA by qRT-PCR in freshly isolated neurons and astrocytes from rats received a 7-week vehicle (young) or D-gal treatment. (H–J), Similar to (G), except that mRNA of CB2, FAAH, and MAGL were measured in (H–J), respectively. Results were from six independent rats with triple wells. Data were normalized to the expression level of CB1 mRNA in neurons from young animals. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with young control in each gene group by Student’s t-test.