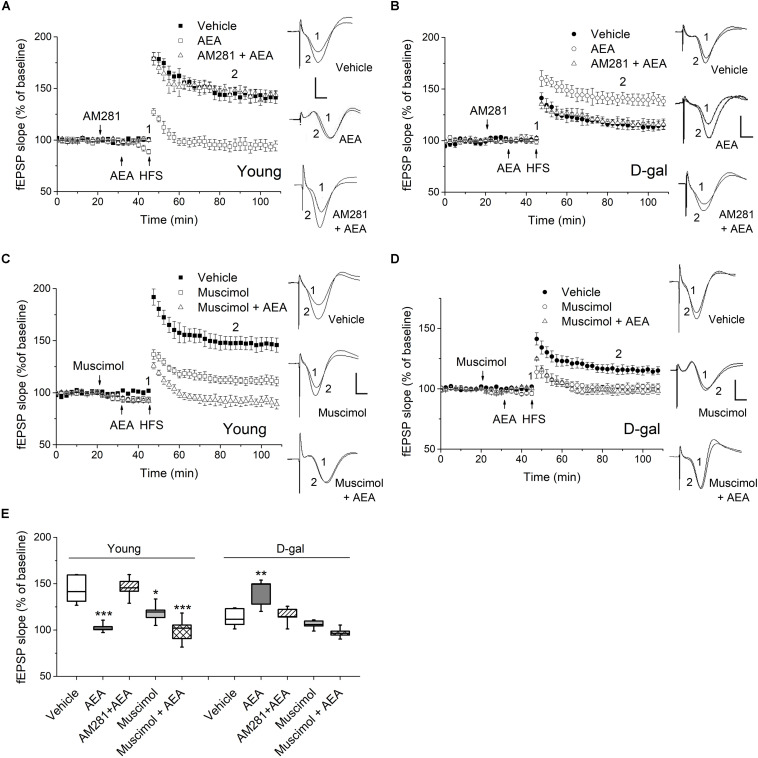
FIGURE 3.
CB1 activation facilitated hippocampal LTP in D-gal-treated rats but impaired LTP in young controls. (A) Time course of LTP with endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA, 1 μM) or vehicle (1% DMSO) applied for 15 min prior to HFS in young rats, or with a 10 min-pretreatment of AM281 (100 μM) followed by the AEA application. Drugs were delivered via intra-CA1 injections. n = 5–6 rats/group Right, Representative fEPSP traces before (1) and 40 min after HFS (2) in young and D-gal-treated animals. (B) Similar to (A), except that D-gal-treated rats was used for this study. Five rats were used in each group. (C) Time course of LTP with a 25 min intra-CA1 injection of 100 μM muscimol, a selective GABA-A receptor agonist, or vehicle (1% DMSO) prior to HFS in young rats, or with a 10 min pretreatment of muscimol followed by a 15 min AEA application. n = 5 rats/group. (D) Similar to C, except that D-gal-treated rats was used for this study. n = 5 rats/group. (E) Quantification of fEPSP slope change showing AEA reduced LTP in young animals but increased LTP in D-gal-treated rats, which was blocked by CB1 antagonist AM281. Pretreatment of muscimol abolished the AEA-induced LTP enhancement in D-gal treated rats. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the vehicle control as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s t-test. Calibration: 5 ms, 0.5 mV.