Fig. 5. Hyperactive mTORC1 causes overreliance on RUVBL1/2 for maintenance of DNA damage stress.
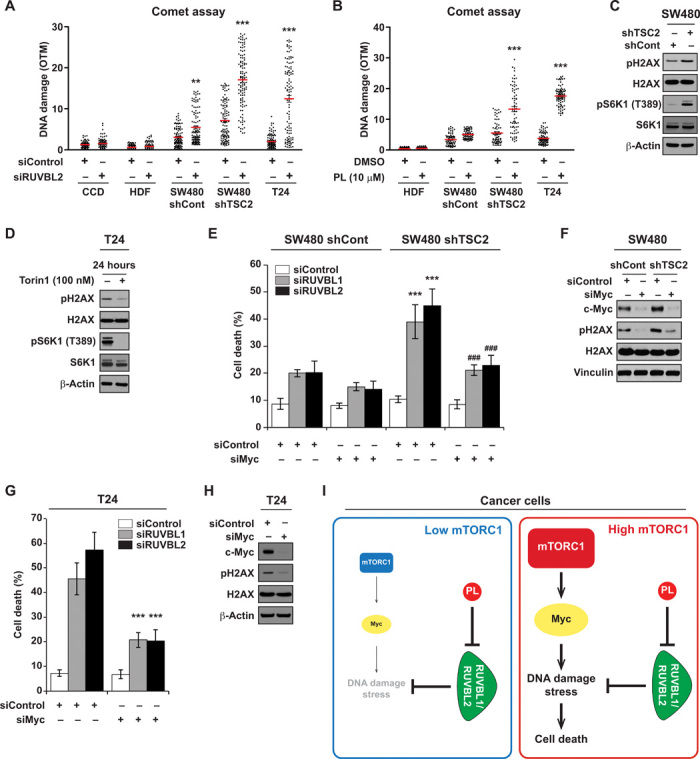
(A) Differential DNA damage induction by RUVBL2 knockdown (siRUVBL2-#1). DNA damage was measured using comet assay. DNA damage was quantified on the basis of the olive tail movement (OTM) value, automatically calculated using a computer program, CometScore. OTM is computed as the summation of each tail intensity integral value, multiplied by its relative distance from the center of the head, and divided by the total comet intensity. A minimum of 80 cells or more were analyzed per group. (B) Differential DNA damage induction by PL. Cells were treated with PL for 14 hours before the occurrence of evident cell death and collected for DNA damage measurement using comet assay. A minimum of 70 cells or more were analyzed per group. DNA damage was quantified on the basis of the OTM value. (C) mTORC1 activity affects DNA damage levels. SW480 cells stably expressing shControl or shTSC2 were analyzed for phospho-histone H2AX (Ser139). Histone H3 and β-actin were used as loading control. (D) T24 cells were harvested 24 hours after Torin1 treatment (100 nM). (E) Depletion of c-Myc reduces RUVBL1/2 silencing–mediated cell death in SW480 cells. Cells were transfected with either siControl or siMyc (si pool) at seeding and were subsequently transfected with siRUVBL1-#2 or siRUVBL2-#1 24 hours after seeding. Cell viability was measured 6 days after transfection. Significant differences between shControl and shTSC2 cells transfected with siRUVBL1/2 (***P < 0.001) and significant differences between shTSC2 cells transfected with siRUVBL1/2-only and siRUVBL1/2 and siMyc (###P < 0.001). (F) SW480 cells infected with shControl or shTSC2 were transfected with siMyc. Cells were lysed 48 hours after transfection, and proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. (G) Depletion of c-Myc reduces RUVBL1/2 silencing–mediated cell death in T24 cells. Cells were transfected with either siControl or siMyc (si pool) at seeding and were subsequently transfected with siRUVBL1-#2 or siRUVBL2-#1 24 hours after seeding. Cell viability was measured 4 days after transfection. (H) T24 cells were analyzed for immunoblot after siMyc transfection (48 hours). (I) Model for synthetic lethality of RUVBL1/2 inhibition in cancer cells with mTORC1 hyperactivation. Cancer cells with high mTORC1 activity have increased DNA damage stress, which is partially through c-Myc. Proper functioning of RUVBL1/2 is critical in mitigating the stress. Blockage of RUVBL1/2 selectively kills cancer cells with high mTORC1 activity. All data are presented as means ± SD. Significant differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA compared with DMSO-treated group for each siRNA treatment (***P < 0.001).
