Fig. 1. Skew scattering mechanisms, basic ARPES, and transport characteristics of KV3Sb5.
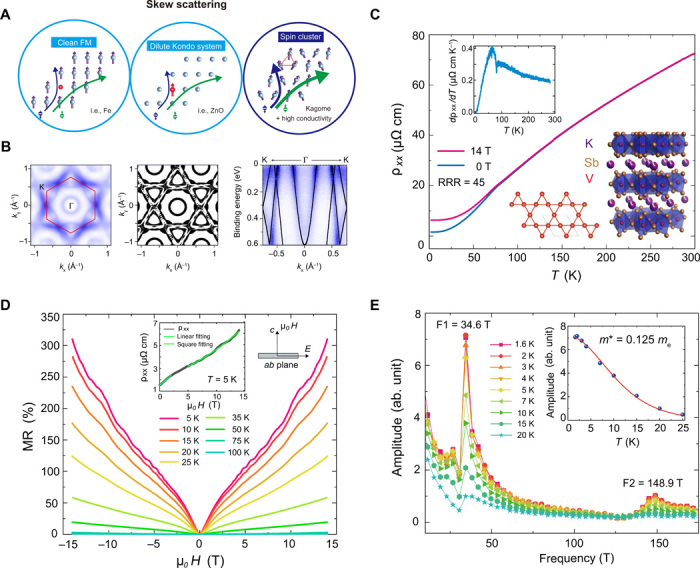
(A) Schematic representation of three different skew scattering mechanisms, including clean ferromagnetic (FM) model, Kondo model, and spin cluster model. (B) Left: Experimentally measured Fermi surface of KV3Sb5. The hexagonal Brillouin zone is marked by the red line. Middle: DFT-calculated Fermi surface. Right: Band dispersion along K-Γ-K direction overlayed with the ARPES measurement. (C) Temperature dependence of longitudinal resistivity in zero field and in a field of 14 T. The inset on the top left shows the temperature dependence of differential longitudinal resistivity in zero field, in which a kink at 80 K corresponds to the magnetic transition. The inset on the bottom right shows the crystal structure of KV3Sb5 and its Kagome lattice. The Residual Resistivity Ratio (RRR) of the sample is 45. (D) MR measured at various temperatures, exhibiting linear field dependence below 3 T and quadratic field dependence at higher field (inset). (E) Extracted FFT frequency showing two identifiable periods of 34.6 and 148.9 T. The inset shows the Lifshitz-Kosevich fit of the 34.6 T orbit with an extracted effective mass of 0.125 me.
