Fig. 5. Full-spectrum life cycle environmental impacts of 1 m2 of the perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell on a logarithmic scale.
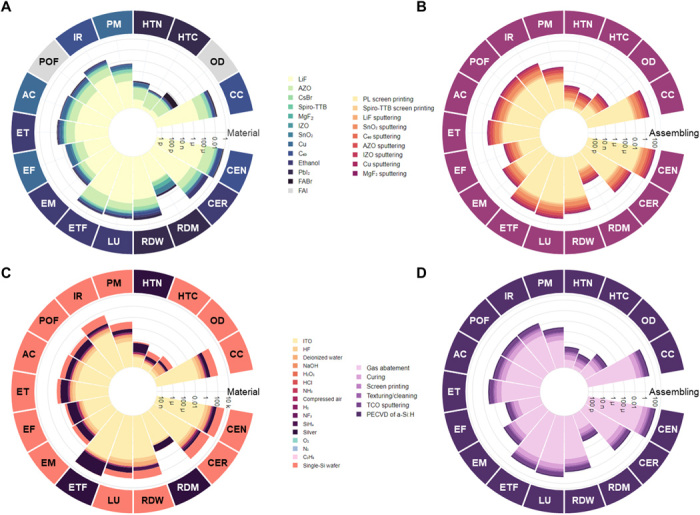
Acronyms go counter clockwise: climate change (CC) (kg CO2 eq); ozone depletion (OD) (kg CFC-11 eq); human toxicity, cancer effects (HTC) (CTUh, c); human toxicity, non-cancer effects (HTN) (CTUh, n-c); particulate matter/respiratory effects (PM) (kg PM2.5 eq); ionizing radiation, human health (IR) (kg U235 eq); photochemical ozone formation (POF) (kg NMVOC eq); acidification (AC) (mol H+ eq); eutrophication, terrestrial (ET) (mol N eq); eutrophication, fresh water (EF) (kg P eq); eutrophication, marine (EM) (kg N eq); ecotoxicity, fresh water (ETF) (CTUe); land use (LU) (kg C deficit); resource depletion, water (RDW) (m3 water eq); resource depletion, mineral, fossil, renewable (RDM) (kg Sb eq); cumulative energy demand, renewable (CER) (MJ eq); cumulative energy demand, non-renewable (CEN) (MJ eq). (A) Life cycle environmental impacts embedded in the raw materials of the add-on. (B) Life cycle environmental impacts associated with the assembling phase of the add-on. (C) Life cycle environmental impacts embedded in the raw materials of the SHJ bottom cell (for both perovskite-silicon tandem and benchmark silicon PVs). (D) Life cycle environmental impacts associated with assembling phase of the SHJ bottom cell (for both perovskite-silicon tandem and benchmark silicon PVs).
