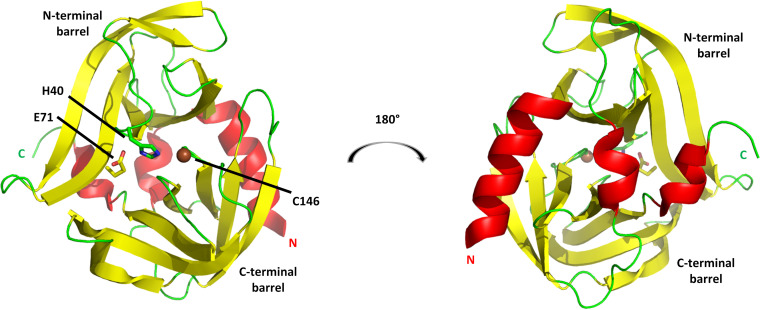
FIG 7.
3Cpro from RV14. The cysteine protease structure consists principally of two six-stranded beta barrels connected by a long linker. (Left) View of the proteolytic active-site face, with the position of the three catalytic triad residues indicated. (Right) View of the opposite face, a surface that consists largely of three helices: a long alpha helix at the N terminus (marked by N), a short 310 helix near the C terminus (marked by C), and a short alpha helix at the center of the linker connecting the N-terminal and C-terminal barrels. This opposite face interacts with RNA and phosphoinositides. Models are colored according to secondary structure: helices are red, beta strands are yellow, and other elements are green. The catalytic C-146 sulfur atom is shown as a brown sphere.