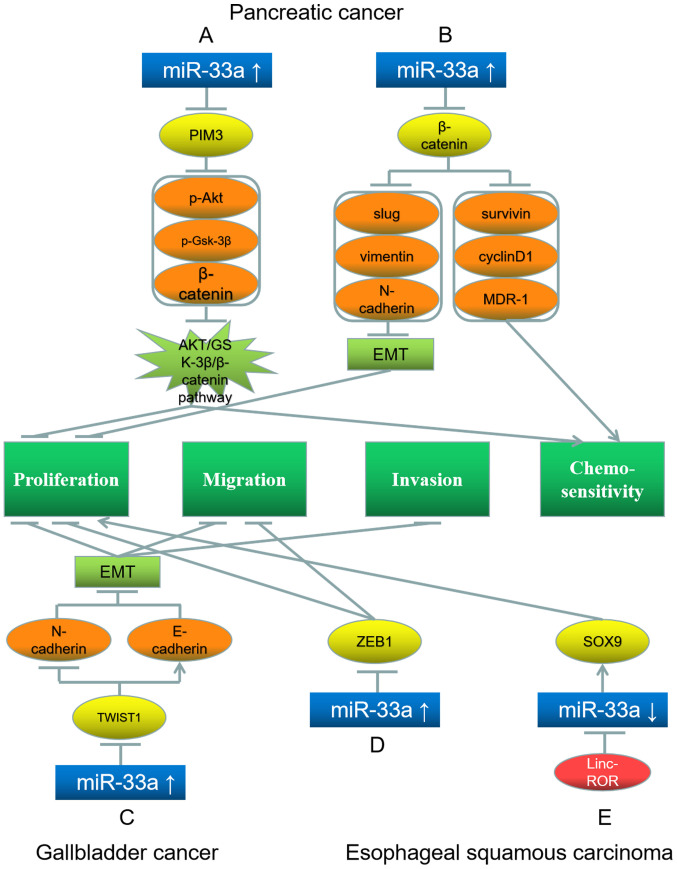
Figure 3.
Roles of miR-33a and its target genes in pancreatic cancer (top), and gallbladder (bottom left) and esophageal squamous (bottom middle and right) carcinoma, and the underlying mechanisms. (A) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene PIM3; this further downregulates p-AKT, p-GSK-3β and β-catenin, leading to proliferation inhibition and chemosensitivity promotion. (B) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene β-catenin, further downregulating slug, vimentin, N-cadherin, survivin, cyclin D1 and MDR-1, leading to EMT inhibition and chemosensitivity promotion. (C) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene TWIST1, further downregulating N-cadherin and upregulating E-cadherin, leading to inhibition of EMT, proliferation, migration and invasion. (D) miR-33a upregulation downregulates its target gene ZEB1, inhibiting proliferation and migration. (E) Linc-ROR downregulates miR-33a, further upregulating its target gene SOX9, which promotes proliferation. Red represents the factor causing miR-33a dysregulation; blue represents miR-33a; yellow represents the target genes of miR-33a; orange represents the downstream proteins; light green represents the signaling pathways and EMT processes; dark green represents the biological processes of cancer cells. miR, microRNA; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; p-, phosphorylated; PIM3, Pim-3 proto-oncogene; GSK, glycogen synthase kinase; MDR-1, multidrug resistance 1; SOX9, SRY-box 9; TWIST1, Twist basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1; ZEB1, Zinc finger E-Box binding homeobox 1.