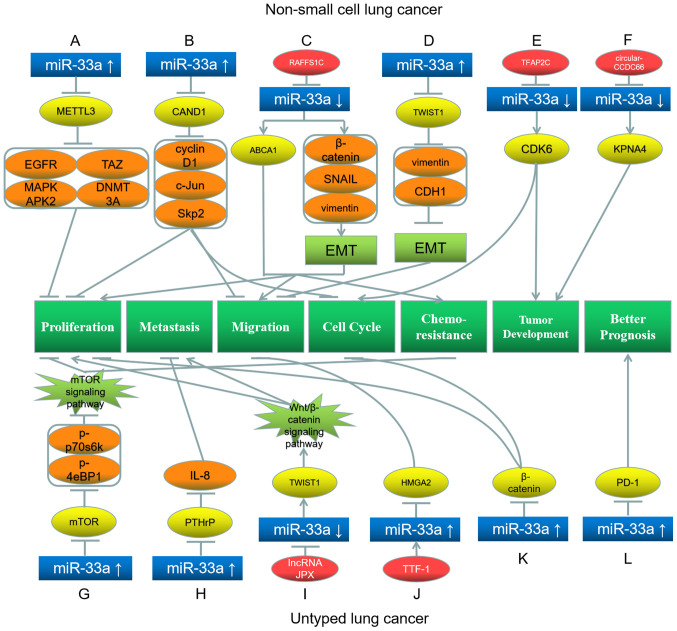
Figure 4.
Roles of miR-33a and its target genes in non-small cell lung cancer (top) and untyped lung cancer (bottom), and the underlying mechanisms. (A) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene METTL3, further downregulating EGFR, TAZ, MAPKAPK2 and DNMT3A, leading to proliferation inhibition. (B) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene CAND1, further downregulating cyclin D1, c-Jun and Skp2, leading to inhibition of proliferation, migration and cell cycle. (C) RAFFS1C inhibits miR-33a and further upregulates its target gene ABCA1, as well as β-catenin, SNAIL and vimentin, leading to promotion of EMT, proliferation, migration and chemoresistance. (D) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene TWIST1, further downregulating vimentin and CDH1, leading to inhibition of EMT and migration. (E) TFAP2C inhibits miR-33a and further upregulates its target gene CDK6, which promotes cell cycle progression and tumor development. (F) circular-CCDC66 inhibits miR-33a and further upregulates its target gene KPNA4, which promotes tumor development. (G) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene mTOR, downregulating p-p70S6K and p-4EBP1, leading to inhibition of proliferation and chemoresistance. (H) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene PTHrP, downregulating IL-8 and leading to metastasis inhibition. (I) lncRNA JPX inhibits miR-33a and further upregulates its target gene TWIST1, leading to promotion of proliferation and metastasis. (J) TTF-1 upregulates miR-33a and further downregulates its target gene HMGA2, which inhibits migration. (K) miR-33a upregulation downregulates its target gene β-catenin, which inhibits proliferation and cell cycle. (L) miR-33a upregulation downregulates its target gene PD-1, resulting in a better prognosis. Red represents the factor causing miR-33a dysregulation; blue represents miR-33a; yellow represents the target genes of miR-33a; orange represents the downstream proteins; light green represents the signaling pathways and EMT processes; dark green represents the biological processes of cancer cells. miR, microRNA; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; p-, phosphorylated; DNMT3A, DNA methyltransferase 3A; MAPKAPK2, mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2; PTHrP, parathyroid hormone-related protein; TAZ, tafazzin; Skp2, S-phase kinase associated protein 2; METTL3, methyltransferase-like 3; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; CAND1, Cullin associated and neddylation dissociated 1; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; TWIST1, Twist basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1; CDH1, cadherin 1; CDK6, cyclin-dependent kinase 6; KPNA4, karyopherin subunit α4; IL-8, interleukin-8; HMGA2, high mobility group AT-hook 2; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1.