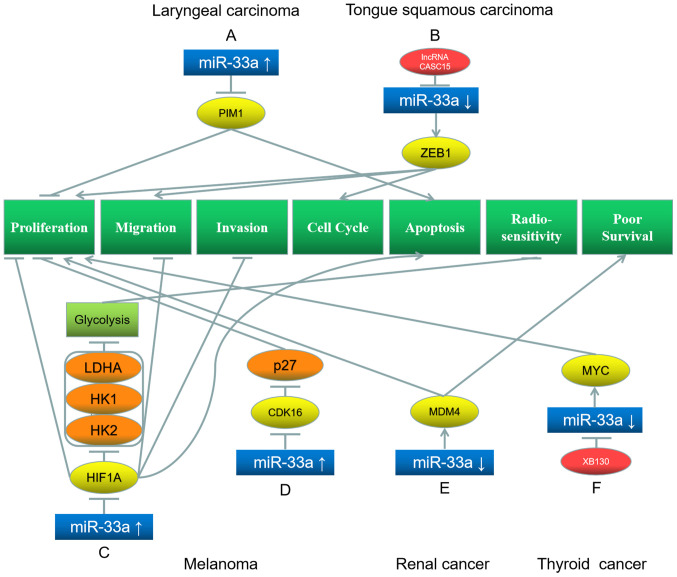
Figure 5.
Roles of miR-33a and its target genes in laryngeal (top left) and tongue squamous (top right) carcinoma, melanoma (bottom left and middle), renal cancer (bottom middle) and thyroid cancer (bottom right), and the underlying mechanisms. (A) miR-33a upregulation downregulates its target gene PIM1, inhibiting proliferation and promotes apoptosis. (B) LncRNA CASC15 downregulates miR-33a and further upregulates its target gene ZEB1, which promotes proliferation, migration and cell cycle. (C) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene HIF1A, downregulating LDHA, HK1 and HK2, leading to inhibition of glycolysis, proliferation, migration, invasion and promotion of apoptosis. (D) miR-33a upregulation inhibits its target gene CDK16, downregulating p27, leading to inhibition of proliferation. (E) miR-33a downregulation upregulates its target gene MDM4, which promotes proliferation and results in poor survival. (F) XB130 downregulates miR-33a and further upregulates its target gene MYC, which promotes proliferation. Red represents the factor causing miR-33a dysregulation; blue represents miR-33a; yellow represents the target genes of miR-33a; orange represents the downstream proteins; light green represents the signaling pathways and EMT processes; dark green represents the biological processes of cancer cells. miR, microRNA; PIM1, Pim-1 proto-oncogene; ZEB1, Zinc finger E-Box binding homeobox 1; HIF1A, hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit α; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A; HK, hexokinase; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; MDM4, mouse double minute 4.