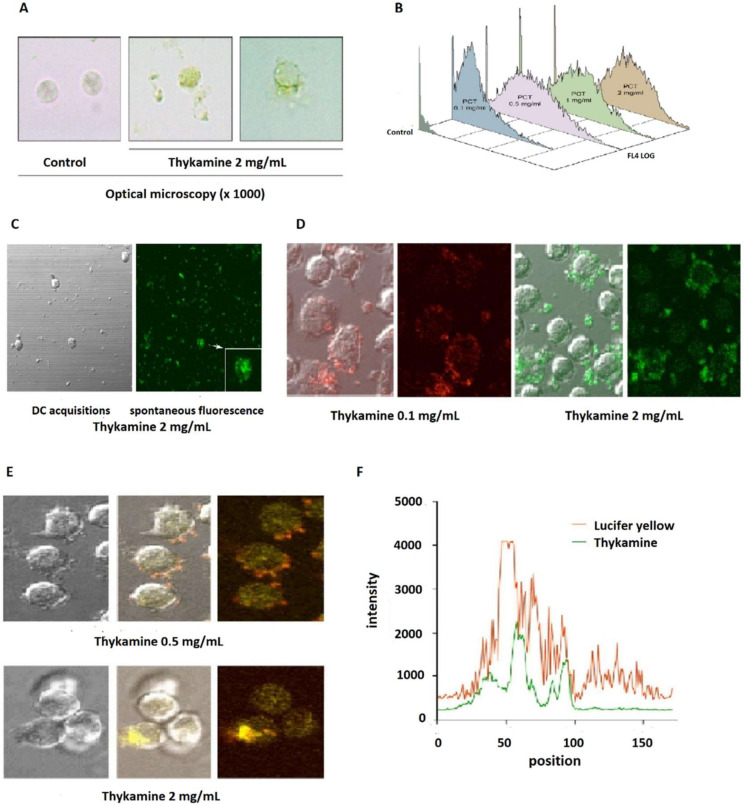
Figure 5.
Morphological characterization of normal human blood neutrophils in the presence of Thykamine at 1000× magnification times. (A,B) granularity measured and visualized by epifluorescence microscopy (A) and by flow cytometry (B) with spontaneous fluorescence of Thykamine. Neutrophils were preincubated with graded concentrations of Thykamine at 37 °C for 30 min. FSC was set on linear scales, SSC and fluorescence channels (FL4) were set on logarithmic scales. (C,D) Confocal microscopy of normal human blood neutrophils pre-treated with Thykamine. Neutrophils were preincubated with different concentrations of Thykamine for 30 min before evaluation by confocal microscopy (Olympus BX-61 confocal laser microscope). (C) the analysis of neutrophils pre-treated with 2 mg/mL Thykamine was performed by using differential interference contrast (DIC) and three-dimensional confocal slices (0.2 µm); the arrow indicates a medial view of a Thykamine-treated neutrophil. (D) Confocal microscopy visualization of human blood neutrophils pre-treated with two different concentrations of Thykamine. (E,F) Characterization of Thykamine entry into human blood neutrophils by the uptake of Lucifer Yellow. Neutrophils were incubated in the simultaneous presence of 0.5 or 2 mg/mL Thykamine and Lucifer Yellow (LY) and Thykamine penetration proceeded for 10 min at 37 °C. (E) visualization of Thykamine and LY was performed with confocal microscopy (Olympus BX-61 confocal laser microscope). (F) computerized comparison of the respective position of Thykamine particles and Lucifer Yellow while penetrating neutrophils. (PCT = Thykamine extract in this figure).