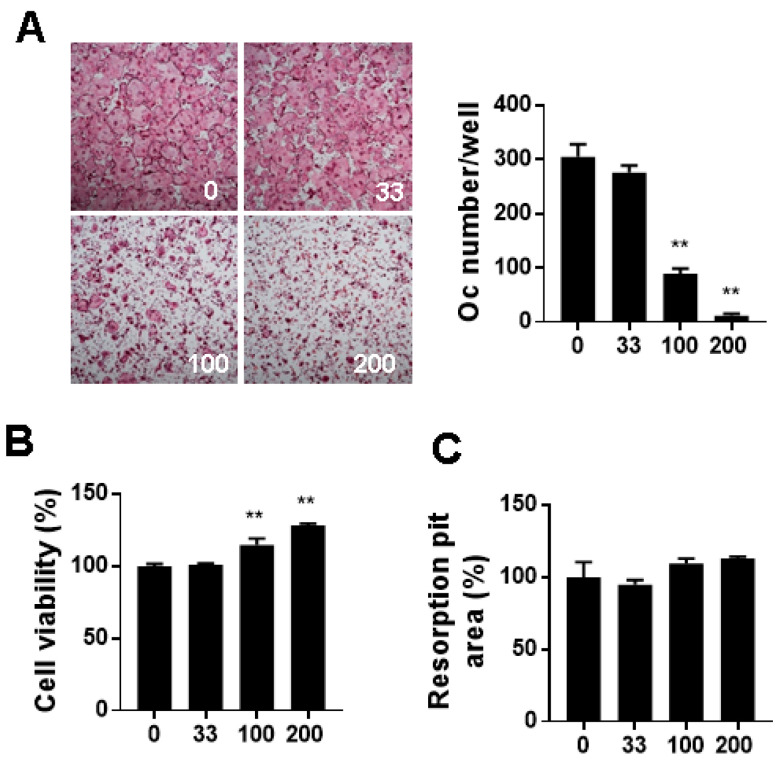
Figure 1.
Inhibitory effects of WELC on osteoclast differentiation. (A) BMMs were cultured with WELC (33 µg/mL, 100 µg/mL, and 200 µg/mL) in the presence of RANKL for 4 days and then stained with TRAP staining solution. Representative images of TRAP-stained osteoclasts at 4× magnification. TRAP-stained multinucleated osteoclasts were enumerated. (B) BMMs were incubated with the indicated concentrations of WELC for 24 h followed by measurement of cell viability using the CCK-8 assay. (C) Mature osteoclasts were cultured with the indicated concentrations of WELC on the bone mimetic surface for 16 h to measure resorption pits. ** p < 0.01 versus vehicle control. BMMs, bone marrow-derived macrophage cells; TRAP, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa Β ligand; WELC, water extract of Lysimachia christinae.