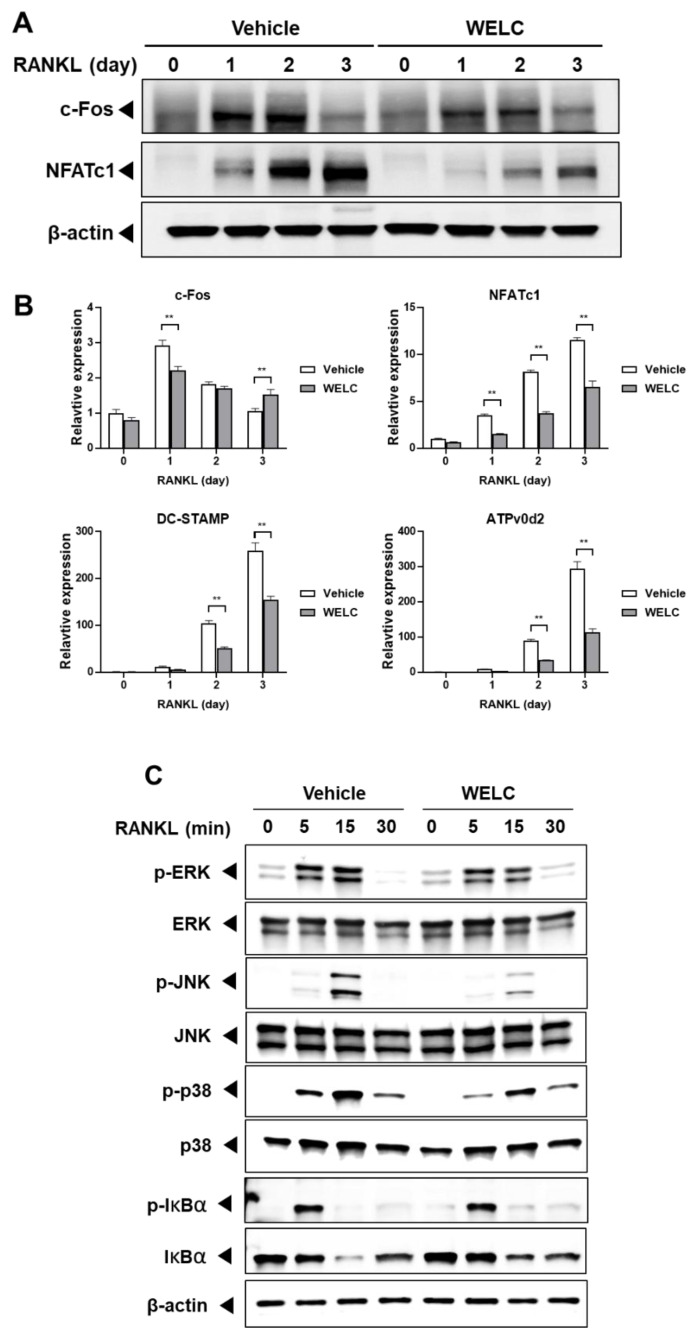
Figure 2.
Inhibitory effects of WELC on RANK signaling pathways. (A,B) BMMs were pretreated with vehicle (distilled water) or WELC (200 µg/mL) and then simulated RANKL (50 ng/mL) for the indicated days. Day 0 represent BMMs untreated with RANKL for 1 day. (A) The protein levels of c-Fos, NFATc1, and β-actin were analyzed by Western blot analysis (B) The relative gene expression levels of c-Fos, NFATc1, DC-STAMP, and ATPv0d2 were analyzed by RT-PCR and expressed as fold change relative to each control (day 0 untreated with WELC). ** p < 0.01 versus vehicle. (C) BMMs were pretreated with WELC for 3 h and then stimulated with RANKL for the indicated times. Protein levels were analyzed by western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. BMMs, bone marrow-derived macrophage cells; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa Β ligand; NFATc1, nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1; DC-STAMP, dendrocyte expressed seven transmembrane protein; Atp6v0d2, ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 38kDa, V0 subunit d2; WELC, water extract of Lysimachia christinae. RT-PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction.