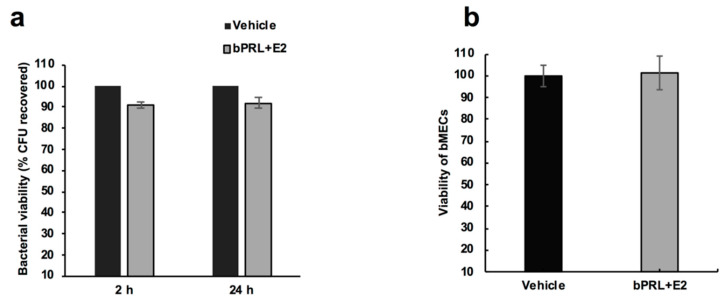
Figure 1.
S. aureus growth and bovine mammary epithelial cell viability in the presence of the combined hormones. (a) Bacterial growth was determined counting the colony forming units (CFU)/mL of S. aureus treated with bovine prolactin (bPRL, 5 ng/mL) and 17β-estradiol (E2, 50 pg/mL) at 2 or 24 h. Each bar shows the mean of triplicates ± SE of three independent experiments (n = 9). The vehicle corresponds to bacteria treated with 1% ethanol. The effect of the vehicle was considered as 100% viability, and the effect of the hormones was normalized with respect to this control. (b) Bovine mammary epithelial cells (bMECs) were cultured with the combined hormones for 24 h and viability was calculated by a trypan blue exclusion assay. The number of viable bMECs is shown. Each bar shows the mean of triplicates ± SE of three independent experiments (n = 9). The effect of the vehicle was considered as 100% viability (1% ethanol).