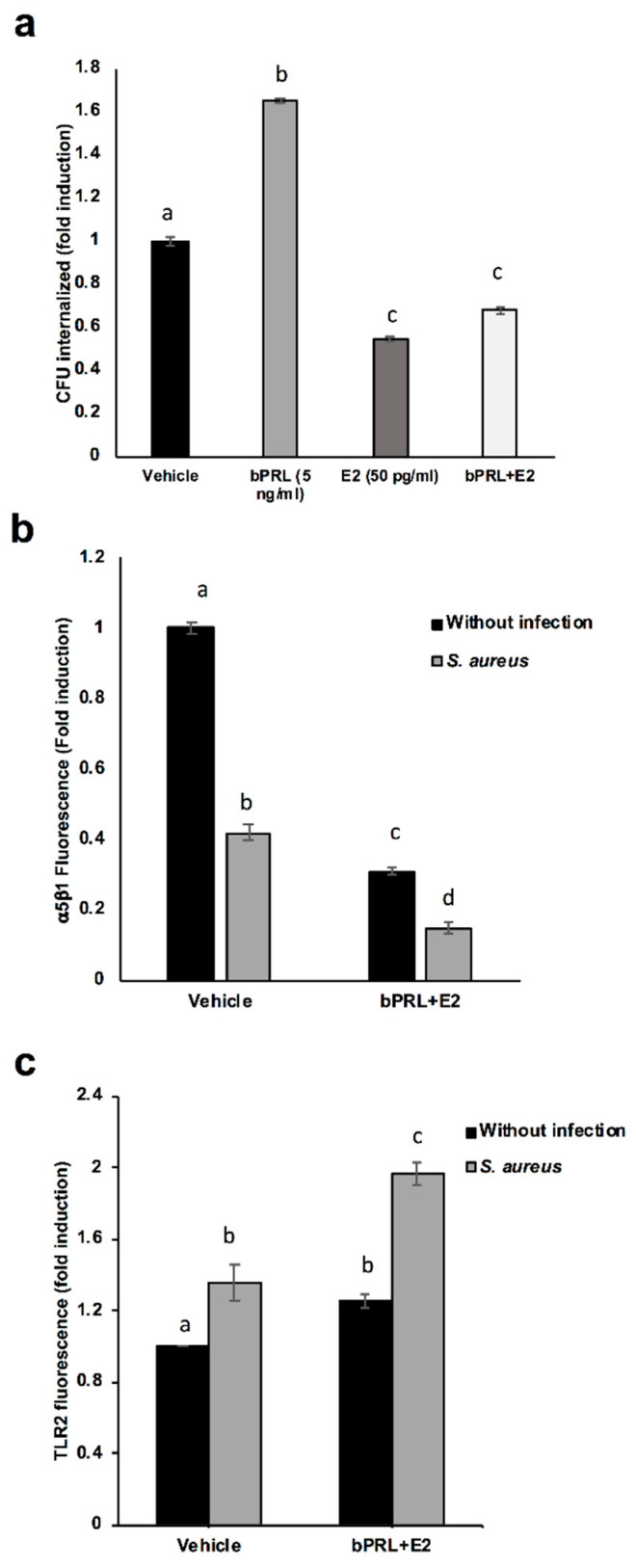
Figure 2.
Effect of the combined hormones on S. aureus internalization: the role of α5β1 integrin and Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2). (a) bMECs were treated with the combined hormones or left untreated (24), and then were challenged with S. aureus for 2 h, and after that were washed three times with PBS and incubated with gentamicin to eliminate extracellular bacteria. Data are shown as the percentage of CFU/mL recovered after bMEC lysis. Values were determined considering the control (bMECs cultured with the vehicle 1% ethanol) as 1. Each bar shows the mean of triplicates ± SE of three independent experiments (n = 9). (b) The relative fluorescence intensity of α5β1 membrane abundance in bMECs treated with the combined hormones and infected with S. aureus is shown. Fluorescence intensity was estimated from 10,000 events. The cells were fixed and stained extracellularly with an anti-α5β1 antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. Each bar shows the mean of the fluorescence of 10,000 events ± SE, considering the fluorescence of control bMECs as 1 (data normalized). Data were obtained from two different experiments, which were run in triplicate (n = 6). (c) The relative fluorescence intensity of TLR2 membrane abundance in bMECs treated with the combined hormones and infected with S. aureus is shown. Fluorescence intensity was estimated from 10,000 events. The cells were fixed and stained extracellularly with an anti-TLR2 antibody and analyzed with flow cytometry. Each bar shows the mean of the fluorescence of 10,000 events ± SE, considering the fluorescence of control bMECs as 1 (data normalized). Data were obtained from two different experiments, which were run in triplicate (n = 6). Different letters between each condition analyzed indicate significant differences (one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey test p ≤ 0.05,) within the treatments.