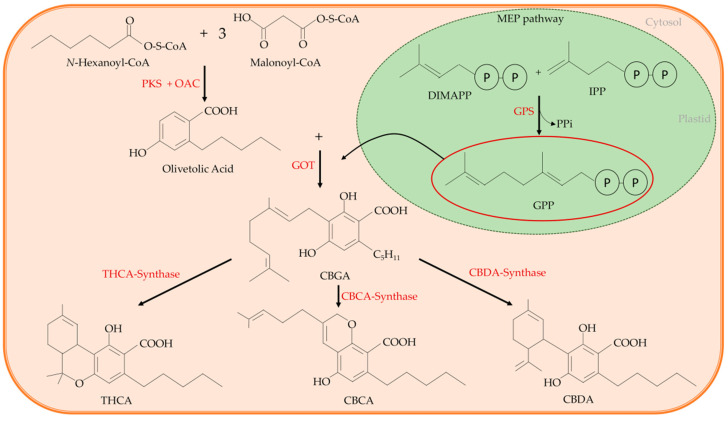
Figure 2.
The cannabinoid synthetic pathway: cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is the common precursor of all main cannabinoids. It is synthesized through an alkylation of the phenolic moiety of olivetolic acid with the terpenoid component of geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP). The reaction is catalysed by a geranylpyrophosphate:olivetolate geranyltransferase (GOT). Olivetolic acid is originated in the cytosolic polyketide pathway through an aldol condensation of hexanoyl-Coenzyme A (CoA) with three molecules of malonyl-CoA, that is catalysed by the polyketide synthase (PKS) enzyme in the presence of olivetolic acid cyclase (OAC). The GPP is synthesized by the plastidial methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. In the cytosol, CBGA is converted into the acidic form of the three main cannabinoids, tetrahydrocannabinol acid (THCA) that in the acidic form has no psychoactive activity, cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and cannabichromenic acid (CBCA). GPS: geranyl pyrophosphate synthase; IPP: isopentenyl diphosphate; OAC: olivetolic acid cyclase.