Figure 4.
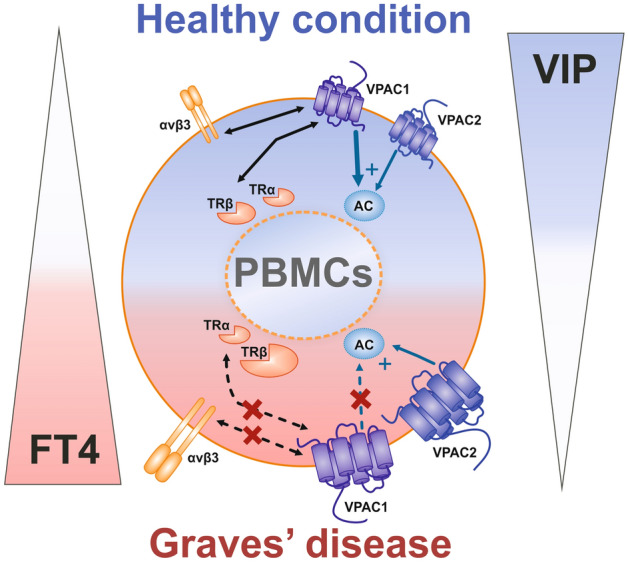
Graphical schematic representation for the proposed inter-relationship between thyroid hormone and VIP system in GD patients. VIP serum levels are significantly lower and negatively correlated with FT4 in hyperthyroid GD patients. Transcript levels of VIP receptors (VPAC1 and VPAC2) and thyroid hormone receptors (nuclear TRβ and plasma membrane αvβ3) are increased in GD patients compared to healthy donors, with the exception of TRα. GD patients show an impairment of VIP signalling through VPAC1 (dotted blue arrows), whereas VPAC2 maintains its capacity to stimulate AC activity (solid blue arrows). There is a correlation between the relative expression of VPAC1 and thyroid hormone receptors in healthy donors (solid black arrows) which is lost in hyperthyroid GD patients (dotted black arrows), suggesting the existence of interactions between both systems in this group of patients. (PBMC peripheral blood mononuclear cell, FT4 free thyroxine 4, AC adenylate cyclase. Blue arrows indicate the contribution of each VPAC receptor signalling to AC activation. Bi-directional black arrows represent correlation between VPAC1 and thyroid hormone receptors).
