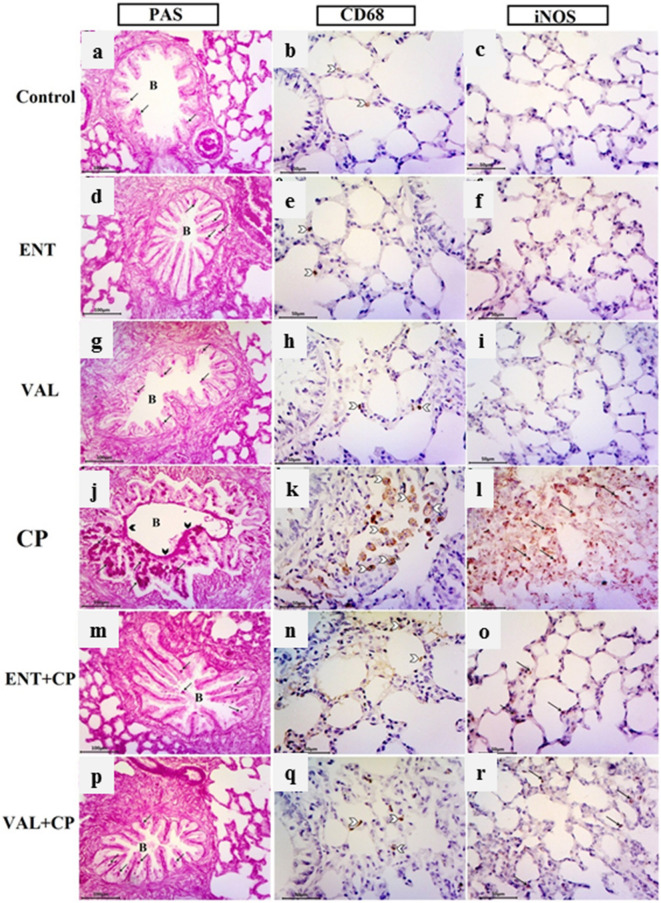
Figure 7.
Photomicrographs of PAS reaction, alveolar macrophages CD68 and iNOS immunohistochemistry in the different groups. ENT (sacubitril/valsartan), CP (cyclophosphamide), VAL (valsartan). Control group (a–c): (a) Normal pattern of PAS-positive reaction in a few goblet cells (arrows) of the bronchialepithelial lining. (b) A few brown positively staining CD68 alveolar macrophages (white arrow head). (c) Undetectable iNOS expression in the alveolar region. ENT and VAL groups (d–i): similar results to the control are noticed .CP-induced rats (200 mg/kg; i.p. single dose on day 5) (j–l): (j) strong PAS reaction in the numerous goblet cells (arrows) of the epithelial lining of bronchi (B). Mucus can be seen clinging to the apical surface of the epithelial lining (black arrow head). (k) Marked dark brown positively stained CD68 alveolar macrophages within the interalveolar septa and in the lumen of alveoli (white arrow head). (l) Marked dark brown iNOS immunoreactive cells (arrows) within the interalveolar septa. ENT + CP (30 mg/kg; p.o. for 6 days and 200 mg/kg; i.p. single dose on day 5, respectively) and VAL + CP groups (15 mg/kg; p.o. for 6 days and 200 mg/kg; i.p. single dose on day 5, respectively) (m–r): (m, p) Nearly normal pattern of PAS-positive goblet cells (arrows) in the lungbronchi. (n, q) Decrease of brown positive stained CD68 alveolar macrophages (white arrow head). (o, r) A few iNOS immunopositive cells within the alveolar and interalveolar tissues (arrows) (PAS technique, X200, alveolar macrophages CD68, X400 & iNOS immunohistochemical staining, X400).