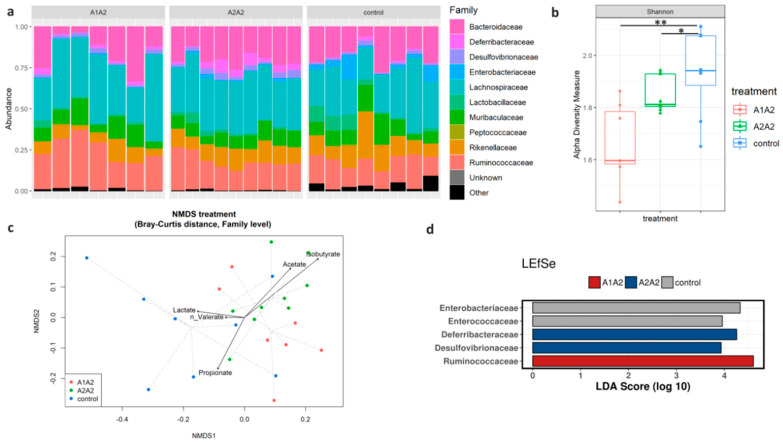
Figure 3.
Family level analysis by Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) of faecal samples of mice fed differently supplemented diets. CTRL, control diet (n = 8); A1A2, milk-based diet with A1/A2 beta-casein variant (n = 7); A2A2, milk-based diet with A2/A2 beta-casein variant (n = 9). (a) Top 10 Families relative abundances. Each bar refers to a single sample. Colour-coding of bacterial families is shown on the right side. “Unknown” includes sequence variants not classified at the family level. “Other” includes the families other than the top 10 for relative abundances. (b) Shannon index boxplots. The lower and upper limits of the box correspond to the first and third quartiles, respectively. The horizontal line within the box represents the median. The vertical line extending from the top of the box indicates the maximum value, while the vertical line extending from the bottom of the box indicates the minimum value. The symbols represent the values for each individual sample. The asterisks indicate significant differences: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (c) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) on Bray–Curtis distance matrix, each point is connected to the centroid group by ‘spider diagram’ (dashed lines). The results from envfit analysis are reported as vectors: the arrow shows an increasing gradient direction and the length of the vector is proportional to the correlation between variable and ordination. (d) LEfSe (Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size) results, the threshold applied for the logarithmic linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score was 2.