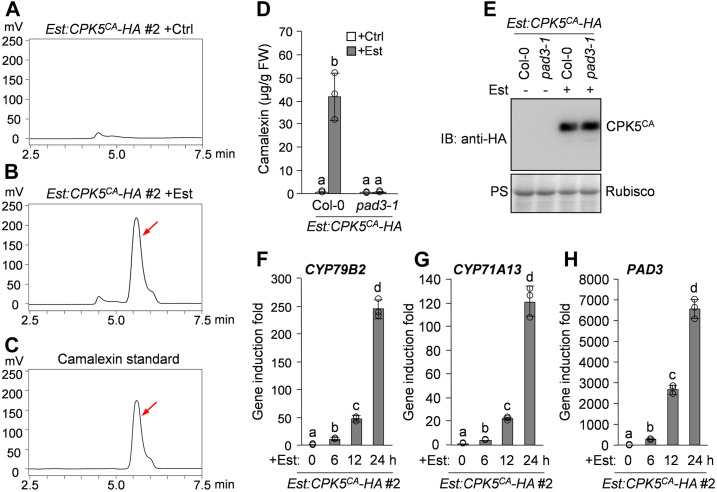
Figure 1.
Conditional Activation of CPK5 Induces Camalexin Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.
(A) to (C) Est-induced expression of CPK5CA in Est:CPK5CA-HA transgenic plants induces camalexin production. Two-week-old Est:CPK5CA-HA seedlings were treated with 10 μM Est (B) or the solvent control (ethanol [Ctrl]; [A]) for 24 h in liquid medium. The metabolites in the medium were analyzed by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Pure camalexin was used as the reference standard (C). Arrows indicate the peak of camalexin.
(D) and (E) CPK5CA-induced camalexin production is abolished in the pad3-1 mutant background. Two-week-old Est:CPK5CA-HA and Est:CPK5CA-HA/pad3-1 seedlings were treated with 10 μM Est or solvent control for 24 h, and camalexin production was quantified (D). The expression levels of CPK5CA-HA were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA antibody, and total protein loading was assessed by Ponceau S staining (PS; [E]). FW, fresh weight.
(F) to (H) Est-induced CPK5CA expression in Est:CPK5CA-HA seedlings leads to the activation of camalexin biosynthetic genes. Two-week-old Est:CPK5CA-HA seedlings were treated with 10 μM Est. Transcript levels of camalexin biosynthetic genes CYP79B2 (F), CYP71A13 (G), and PAD3 (H) at the indicated time points were analyzed by RT-qPCR.
In (D), (F), (G), and (H), error bars indicate sd (n = 3 biological repeats), small circles represent individual data points, and different letters above the columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), as determined by one-way ANOVA.