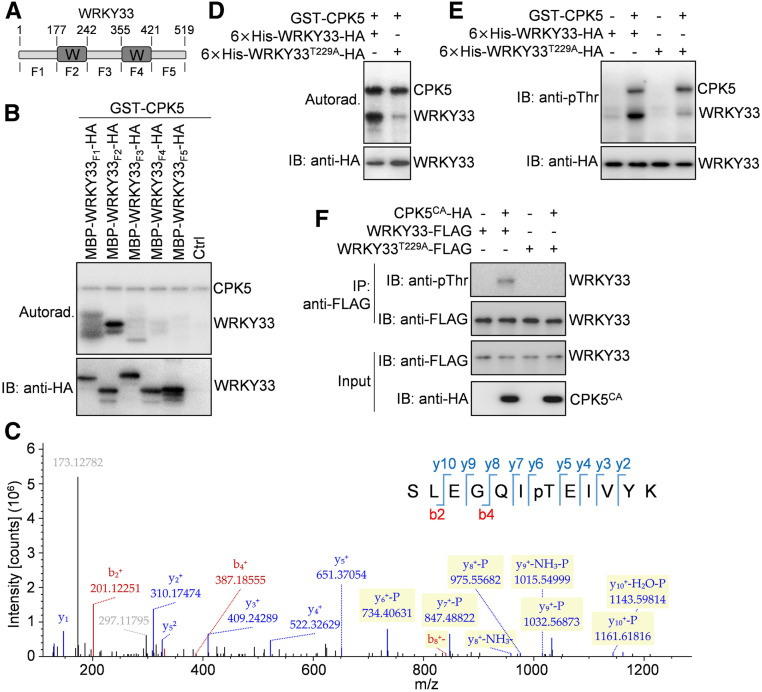
Figure 5.
CPK5 Phosphorylates the Thr-229 Residue of WRKY33.
(A) Schematic diagram showing the domain structure of WRKY33 protein. WRKY33 contains two WRKY domains (W) and three other regions of unknown function. The amino acid positions are labeled on the top. The fragments of WRKY33 used for the following experiments are indicated at the bottom.
(B) The N-terminal WRKY domain of WRKY33 is phosphorylated by CPK5. Phosphorylation of the MBP/HA-tagged WRKY33 fragments by GST-CPK5 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP was detected by autoradiography (Autorad.; top panel). The protein inputs were assessed by immunoblotting (IB; bottom panel).
(C) The Thr-229 residue of WRKY33 is phosphorylated by CPK5. An LC-MS/MS analysis of the phosphorylation reaction containing GST-CPK5 and MBP-WRKY33F2-HA proteins revealed the phosphorylation of Thr-229 in WRKY33F2 by CPK5.
(D) and (E) The Thr-229 residue is the major CPK5 phosphorylation site in WRKY33 in vitro. Phosphorylation of the wild-type and T229A mutant forms of 6×His-WRKY33-HA proteins by GST-CPK5 in the presence (D) or absence (E) of [γ-32P]ATP was detected by autoradiography (D) or immunoblotting (E), respectively (top panels). The protein inputs were assessed by immunoblotting (bottom panels).
(F) Mutation of Thr-229 in WRKY33 blocked its phosphorylation by CPK5CA in Arabidopsis protoplasts. The wild-type and T229A mutant forms of WRKY33-FLAG proteins were coexpressed with CPK5CA-HA in protoplasts. The WRKY33-FLAG proteins immunoprecipitated from protoplast extracts using anti-FLAG agarose beads (IP: anti-FLAG) were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-pThr (IB: anti-pThr) or anti-FLAG (IB: anti-FLAG) antibody (top two panels). The protein inputs were assessed by immunoblotting (bottom two panels).