Figure 7. S100A6 contributes to the PPP5C-FKBP51-mediated regulation of calcium entry and endothelial barrier function.
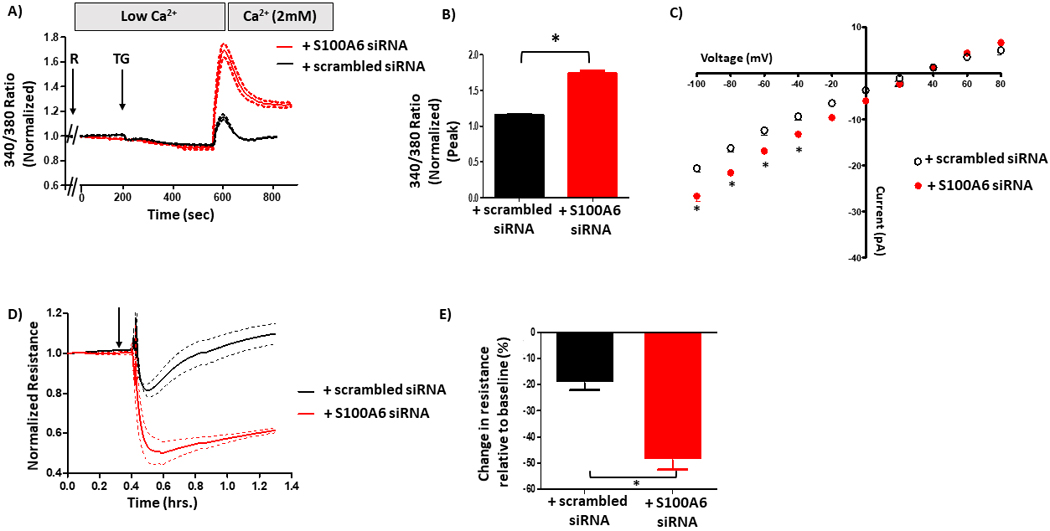
A. Global calcium entry was measured in FKBP51 over-expressing PMVECs in which S100A6 expression was suppressed. The decrease in calcium entry following rolipram (R) + thapsigargin (TG) in FKBP51 over-expressing cells was reversed upon S100A6 suppression. B. Comparison of peak calcium entry observed. Peak calcium entry was increased by 34% in cells treated with S100A6 siRNA as compared to cells treated with scrambled siRNA. n = 3 independent experiments. C. ISOC was measured. The decrease in ISOC in FKBP51 over-expressing cells treated with scrambled siRNA was reversed in cells treated with S100A6 siRNA as evidenced by increased current. n = 4 measurements per condition from 3 different siRNA treatments performed over two different recording periods. D. ECIS® was performed to assess the endothelial barrier. The attenuated decrease in resistance following R + TG in FKBP51 over-expressing cells was reversed upon S100A6 suppression. E. Comparison of peak resistance decrease observed in D. The peak resistance decrease was greater in FKBP51 over-expressing cells treated with S100A6 siRNA compared to cells treated with scrambled siRNA. n = 3 independent experiments.
