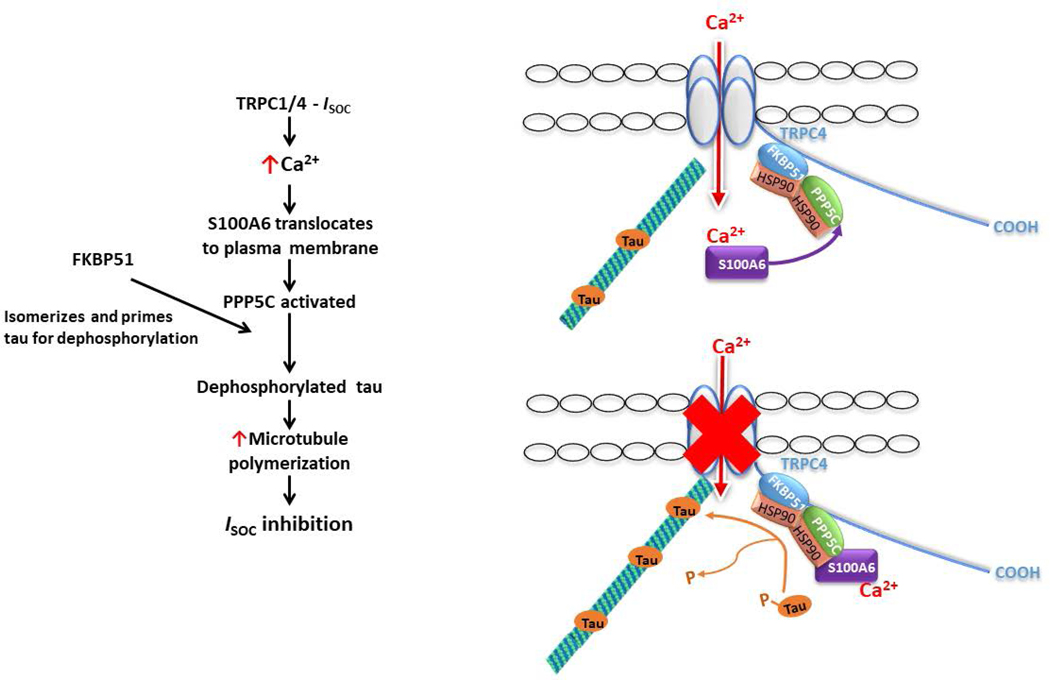
Figure 8. Model of the mechanism by which S100A6 and the PPP5C-FKBP51 axis inhibit ISOC.
Upon activation of ISOC, calcium enters the cell and binds to S100A6 to induce translocation of S100A6 to the plasma membrane to interact with the ISOC channel heterocomplex. Within the ISOC heterocomplex reside PPP5C and FKBP51. FKBP51 isomerizes tau and primes it for dephosphorylation by PPP5C. Dephosphorylated tau is then able to bind to microtubules to promote polymerization which is responsible for inhibition of channel function.