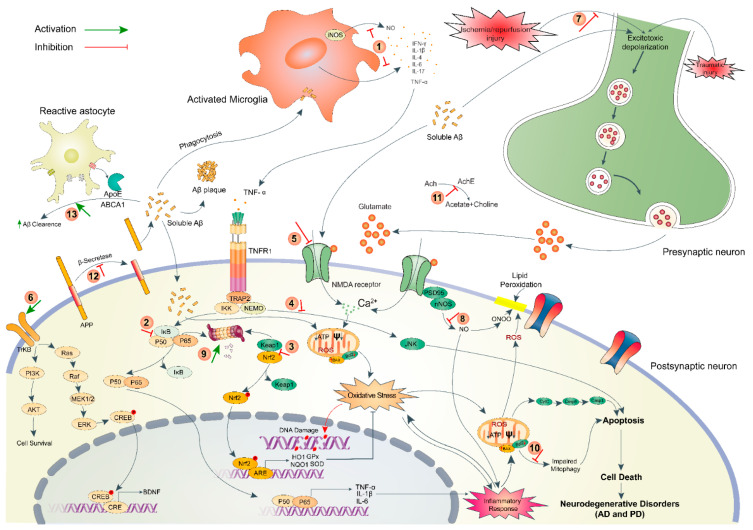
Figure 5.
A scheme highlighting the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disorders and post-ischemic consequences along with indicating the underlying mechanism of neuroprotective action of algal compounds. The numeric symbols indicate the points of pharmacological action that include (1) inhibition of cytokine secretion from activated microglia by fucoxanthin, fucosterol, fucoidan, dieckol, phlorofucofuroeckol and bieckol, κ-carrageenan, floridoside and seleno-polymannarate, (2) attenuation of inflammatory response via inhibition of NF-κB pathway by eckol, dieckol and 8,8-bieckol, (3) priming of antioxidant defense system via activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway (blocking interaction between Nrf2 and Keap1) by fucoxanthin, fucoidan and zonarol, (4) Reduction of apoptosis via inhibiting pro-apoptotic JNK/Erk pathway by dimethylsulfoniopropionate and κ-carrageenan-derived pentasaccharide, (5) Inhibition of glutamate-induced Ca2+ influx via blocking extrasynaptic GluN2B by fucoidan and tramiprosate, (6) Activation of BDNF-dependent pro-survival pathway via inducing PI3K/Akt or TrkB/ERK signaling by fucoxanthin and fucosterol, (7) Attenuation of I/R-injury via preventing excitotoxic depolarization by C-phycocyanin, (8) Inhibition of nNOS sequestration by tramiprosate, (9) proteasomal degradation by fucoidan, (10) Induction of autophagy/mitophagy by fucoxanthin, (11) anticholinesterase activity by fucoidan, fucoxanthin, dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol, (12) anti-amyloidogenesis via blocking β-secretase activity by fucoxanthin, fucosterol and glycoprotein, and (13) Aβ-clearance via enhancing the transcription of ApoE and ABC transporters genes by fucosterol, saringasterol, and alginate-derived oligosaccharide. NF-κB/p50-pp65, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ARE, antioxidant response element; IkB, inhibitor of NF-κB; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; GluN2B, N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; Akt, protein kinase B; MEK1/2, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; TrkB, tropomyosin receptor kinase B; CREB, cAMP-response element binding protein; CRE, cAMP response elements; BDNF, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; AChE, acetylcholinesterase; Ach, acetylcholine; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ψ, mitochondrial membrane potential.