Figure 4.
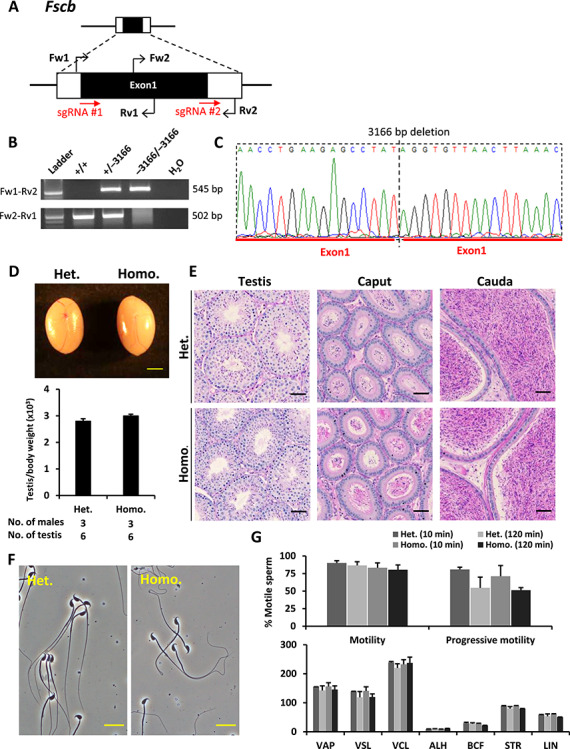
Phenotypic analysis of Fscb knockout male mice. (A) Genomic structure and knockout strategy of mouse Fscb. Two sgRNAs were designed to target the 5′ and the 3′ region, respectively, of the coding exon (Exon 1). Four primers (Fw1, Fw2, Rv1, and Rv2) were designed for genotyping. (B) Mutant and wild-type alleles were detected by genomic PCR using primer sets Fw1–Rv2 and Fw2–Rv1, respectively. (C) DNA sequence of the knockout allele was determined by Sanger sequencing. (D) Testis appearance and testis to body weight ratios of Fscb heterozygous and homozygous knockout mice. Scale bar = 2 mm. (E) Histological analyses of testes and epididymides in Fscb heterozygous and homozygous knockout mice. Scale bars = 50 μm. (F) Morphology of cauda epididymal spermatozoa in Fscb heterozygous and homozygous knockout mice. Scale bars = 20 μm. (G) Analysis of sperm motility in Fscb heterozygous and homozygous knockout mice. Sperm motility and kinetic parameters were measured at 10 and 120 min of incubation in TYH media.
