Figure 5.
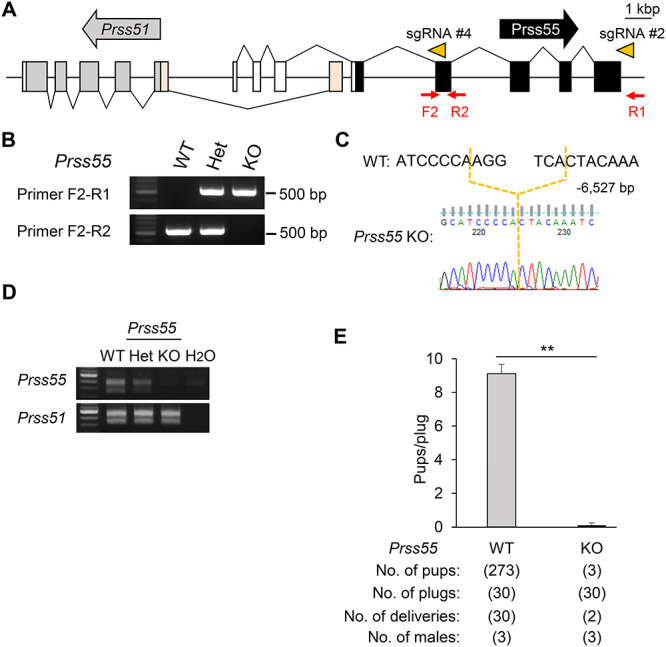
Male mice lacking Prss55 have severe fertility defects. A. Genomic structure and KO strategy of mouse Prss55 KO mice. The direction of the arrows, in gray (Prss51) and black (Prss55), indicates the direction of transcription. The direction of the arrowheads (orange) indicates the direction of sgRNA (#2 and #4). Gray boxes, Prss51 coding region; light orange boxes, Prss51 noncoding region; black boxes, Prss55 coding region; white boxes, Prss55 noncoding region. F2, forward primer for genotyping; R1 and R2, reverse primers for genotyping. Scale bar, 1 kbp. B. Genotyping with genomic PCR. Primers shown in panel A were used for PCR. WT, wild type; Het, heterozygous; KO, Prss55 homozygous KO. C. DNA sequencing. The sequence of the PCR amplicon was analyzed. A region of 6527 bp was deleted in Prss55 KO mice. D. The expression of mouse Prss51 and Prss55 was examined by RT-PCR using RNA isolated from testes. WT, wild type; Het, heterozygous; KO, Prss55 homozygous KO. E. Fertility is presented pups/plug: the number of total pups born divided by the number of vaginal plugs in females after natural mating (9.1 ± 0.6 for WT females mated with WT males, and 0.1 ± 0.1 with Prss55 KO males). **P < 0.01. Error bars, mean ± SD.
