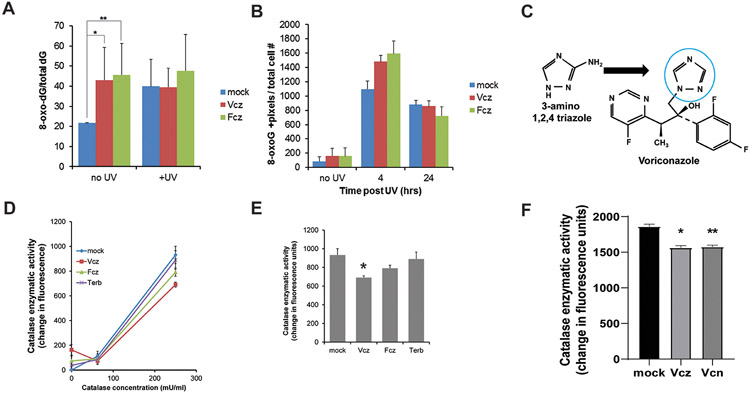
Figure 3. Triazole antifungal agents promote UV-induced 8-oxo-dG formation in vitro by inhibiting catalase.
PHKs were cultured with 25 μM Vcz, 25 μM Fcz, or vehicle for 24 hours and then UV irradiated (25 mJ/cm2). A) PHKs were assayed for cellular 8-oxo-dG using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. In the absence of UV, PHKs exposed to Vcz and Fcz contained higher levels of 8-oxo-dG than controls. Error bars show SEM. N=3. Mock vs. Vcz, *p = 0.04, mock vs. Fcz, **p = 0.05, mock vs mock + UV, p = 0.03. Post-UV, levels of 8-oxo-dG plateau in all conditions. B) Immunofluorescent staining for 8-oxo-dG was performed on the PHKs subjected to the experimental conditions described in A. 8-oxo-dG positive staining signal was determined using image analysis software. Error bars show SEM. N=3. At four hours, mock vs Vcz, *p = 0.01, and mock vs Fcz, **p = 0.03. C) Structural comparison of 3-amino 1,2,4 triazole, a triazole known to inhibit catalase, and the triazole moiety in voriconazole (blue circle) (38). D) Vcz inhibits catalase enzymatic activity as determined using a fluorescent in vitro assay described in methods. Fcz weakly inhibits catalase while terbinafine did not inhibit catalase significantly compared to controls. Error bars show SEM. N=3. E) Graphical representation of catalase assay data from the 250 mU/mL concentration of enzyme. Mock vs Vcz, * p = 0.01, mock vs Fcz, p = 0.07, Vcz vs Fcz, p = 0.03, mock vs terbinafine, p = 0.35. F) Graphical representation of catalase assay data from the 250 mU/mL concentration of enzyme 30 minute time point. Error bar is SEMMock vs Vcz, * p = 0.011, mock vs Vcn, **p = 0.013, Vcz vs Vcn, p = 0.38.