Figure 1.
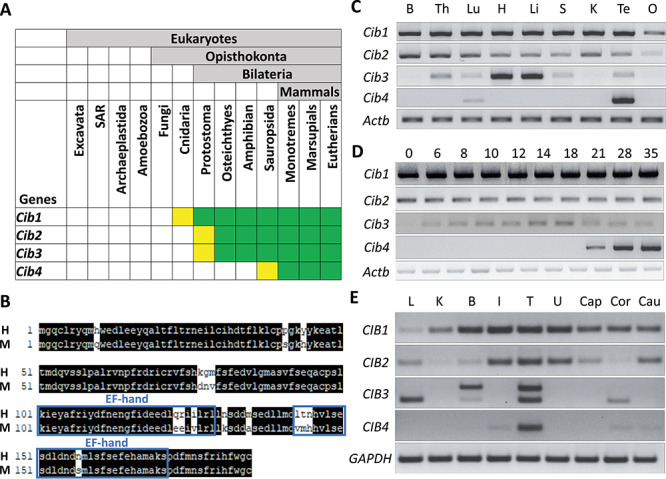
CIB4 is testis-enriched in mice and humans. (A) Conservation of CIB family. Green indicates presence of CIB in most species within taxon. Yellow indicates loss in several species within taxon. (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences between mice and human. Matched sequences are highlighted in black, and EF-hands are indicated in blue boxes. H: human CIB4, M: mouse CIB4. (C) Expression of mouse Cib family members was analyzed by RT-PCR using various organs. Actb was used as an RNA expression control. B: brain, Th: thymus, Lu: lung, H: heart, Li: liver, S: spleen, K: kidney, Te: testis, O: ovary. (D) Expression of mouse Cib family members was analyzed by RT-PCR using various postnatal testes. Actb was used as an RNA expression control. (E) Expression of the human CIB family members was analyzed by RT-PCR using various organs. Two bands were observed for CIB3 likely due to the existence of variants. GAPDH was used as an RNA expression control. L: liver, K: kidney, B: brain, I: intestine, T: testis, U: uterus, Cap: caput epididymis, Cor: corpus epididymis, Cau: cauda epididymis.
