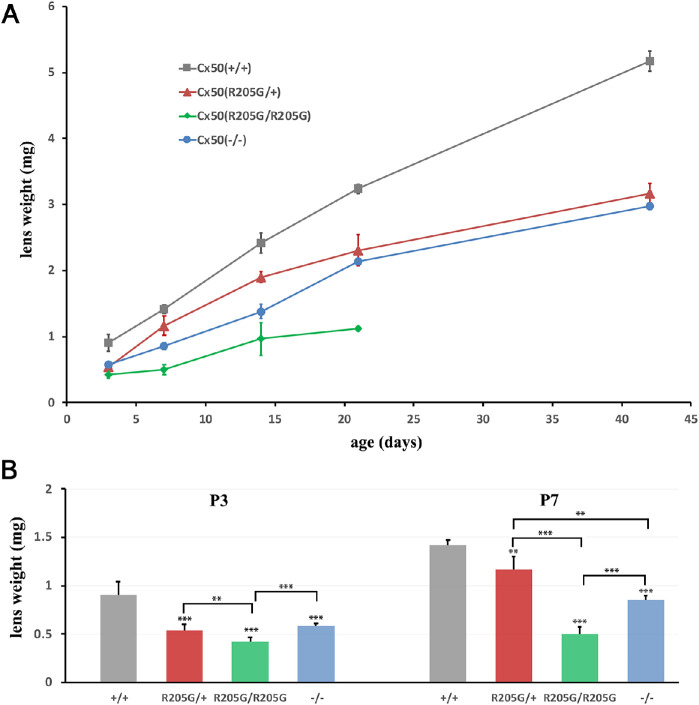
Figure 2.
The lens growth curves of Cx50(+/+) wild-type, Cx50(–/–) knockout, heterozygous Cx50(R205G/+), and homozygous Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses based on the lens wet weight at postnatal ages. (A) Individual wet lens weight was measured, and the average lens wet weight was obtained from mice of each genotype (n = 3–7 mice). The average lens weight for each genotype was plotted at each age point from P3 to P42 days. The Cx50-R205G mutation displays a semidominant inheritance pattern, in which the heterozygous Cx50(R205G/+) lenses are smaller than the wild-type Cx50(+/+) lenses, while the homozygous Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses are the smallest. (B) Statistical analysis and the wet weight bar graphs of different lenses at P3 and P7. Compared to the wild-type lenses, the P3 Cx50(–/–) lenses have approximately 36% reduction (P < 0.001), heterozygous Cx50(R205G/+) lenses show approximately 41% reduction (P < 0.001), and homozygous Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses display approximately 54% reduction (P < 0.001); at P7, the Cx50(–/–) knockout lenses show approximately 40% reduced weight (P < 0.001), the heterozygous Cx50(R205G/+) lenses have approximately 18% reduction (P < 0.01), and homozygous Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses have approximately 65% reduction (P < 0.001). The mean values per data point are presented as ± SD (n = 3–10 mice). Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, indicating statistically significant for the comparison.