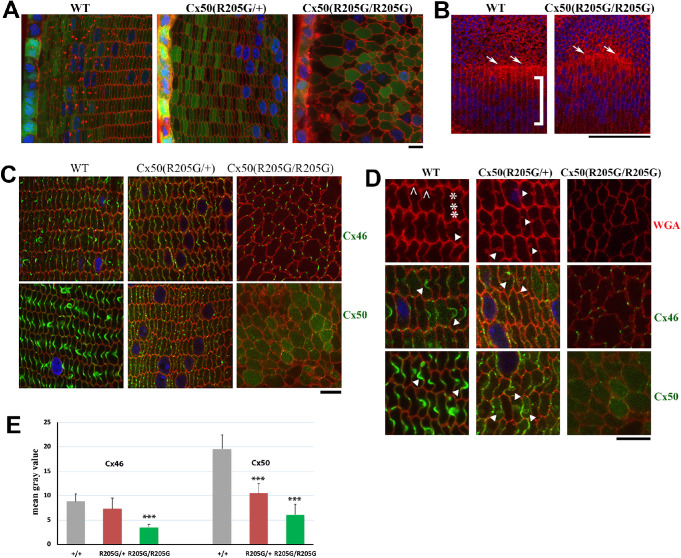
Figure 6.
The Cx50-R205G mutation disrupts meridional rows and fulcrum at lens equator and alters lens fiber cell shape and gap junctions. (A) Lens fiber cell morphology revealed by wheat germ agglutinin (WGA; red) and DAPI (blue) stained cross sections of GFP-positive (green) Cx50(+/+) wild-type, Cx50(R205G/+), and Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses from 3-week-old mice. Images collected from the lens periphery to interior 100-µm fibers are displayed. The heterozygous Cx50-R205G lens fiber cells show hexagonal cell shape with normal fiber-to-fiber overlay organization while homozygous Cx50-R205G lens fiber cells display rounded cell shape and irregular organization. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B) Equatorial images of P13 wild-type and Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses stained with WGA (red) and DAPI (blue). In the wild-type lens, meridional rows (indicated by ]) are aligned and straight, but the meridional rows of Cx50(R205G/R205G) lenses are misaligned. The Cx50(R205G/R205G) lens fulcrum (indicated by white arrows) is disrupted, unlike the straight line of the wild-type lens fulcrum (white arrows). Scale bar: 100 µm. (C) Cx46 and Cx50 gap junction expression in lens sections costained with either anti-Cx46 or anti-Cx50 antibodies (green), WGA (red), and DAPI (blue). In the wild-type lens, Cx46 and Cx50 gap junction plaques are enriched in the ball-and-sockets and also expressed on the long and narrow sides of fibers. Heterozygous Cx50-R205G fiber cells display reduced and short or small gap junction plaques along the broad and short sides, while the homozygous Cx50(R205G/R205G) fibers only have sparse, very short, or dot-like Cx46 and Cx50 plaques. All lens sections were from 3-week-old mice. Scale bar: 10 µm. (D) Enlarged images of lens fibers costained with anti-Cx46 or anti-Cx50 (green), WGA (red), and DAPI (blue). Typical Cx46 and Cx50 gap junctions are detected in wild-type ball-and-sockets (indicated by white arrowheads) while short or dot-like Cx46 and Cx50 signals are observed in Cx50(R205G/+) fiber cell boundaries with aberrant membrane structures (indicated by arrowheads). The caret indicates the short side of the hexagonal shaped fibers in the wild-type, while the asterisk marks the long side. All lens sections were from 3-week-old mice. Scale bar: 10 µm. (E) Bar graphs of Cx46 and Cx50 staining intensity quantitation. Compared with the wild-type lens section staining, the Cx50(R205G/R205G) section shows significantly reduced Cx46 (P < 0.001) and Cx50 (P < 0.001) staining intensity; the heterozygous Cx50(R205G/+) displays significantly reduced Cx50 staining intensity (P < 0.001) compared with the wild-type, but the difference of Cx46 staining intensity between the heterozygous and wild-type is not statistically significant (P = 0.27). Data are shown as mean ± SD, Student’s t-test, ***P < 0.001, indicating statistically significant when compared with the wild-type.