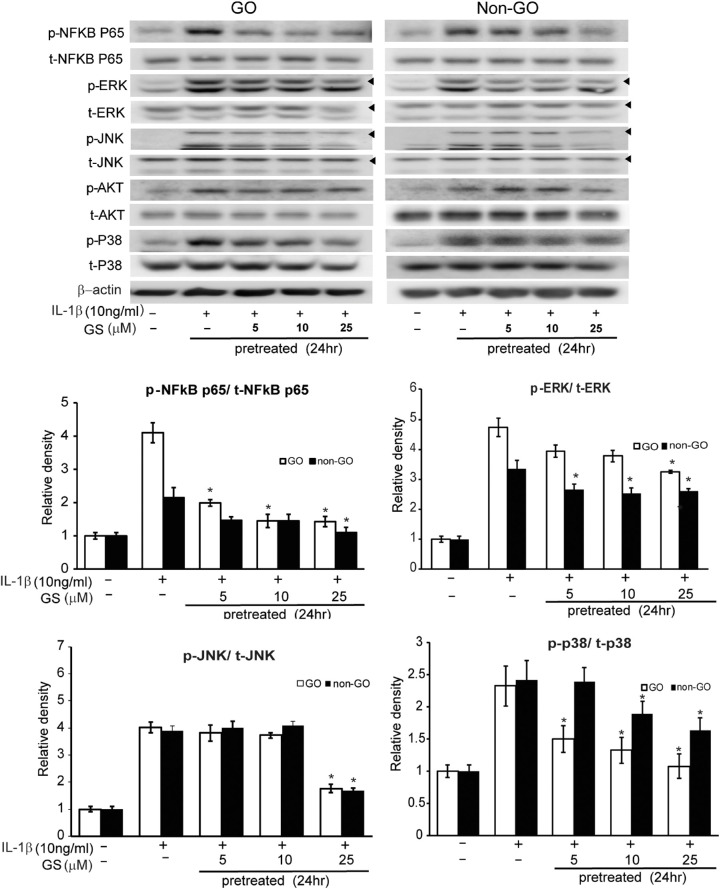
Figure 6.
Effect of GS on intracellular signaling pathways in GO and non-GO cells. Cells from GO (n = 3, white column) and non-GO (n = 3, black column) were treated with various concentrations of GS (5–25 µM) for 24 hours prior to stimulation with 10 ng/mL IL-1β for 1 hour. GS cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting to evaluate phosphorylated NF-κB p65, ERK, JNK, Akt, and p38 protein expression. Treatment of GS significantly attenuated IL-1β-induced activation of p-NF-kB protein in both GO and non-GO cells in a dose-dependent manner. P-ERK, p-JNK, and p-p38 were significantly inhibited by GS in both GO and non-GO cells; however, p-Akt signaling was not altered by GS. The data in the columns are the mean relative density ratio (phosphorylated form/total form) ± SD of three experiments (*P < 0.05 vs. IL-1β stimulated cells without GS pretreatment).