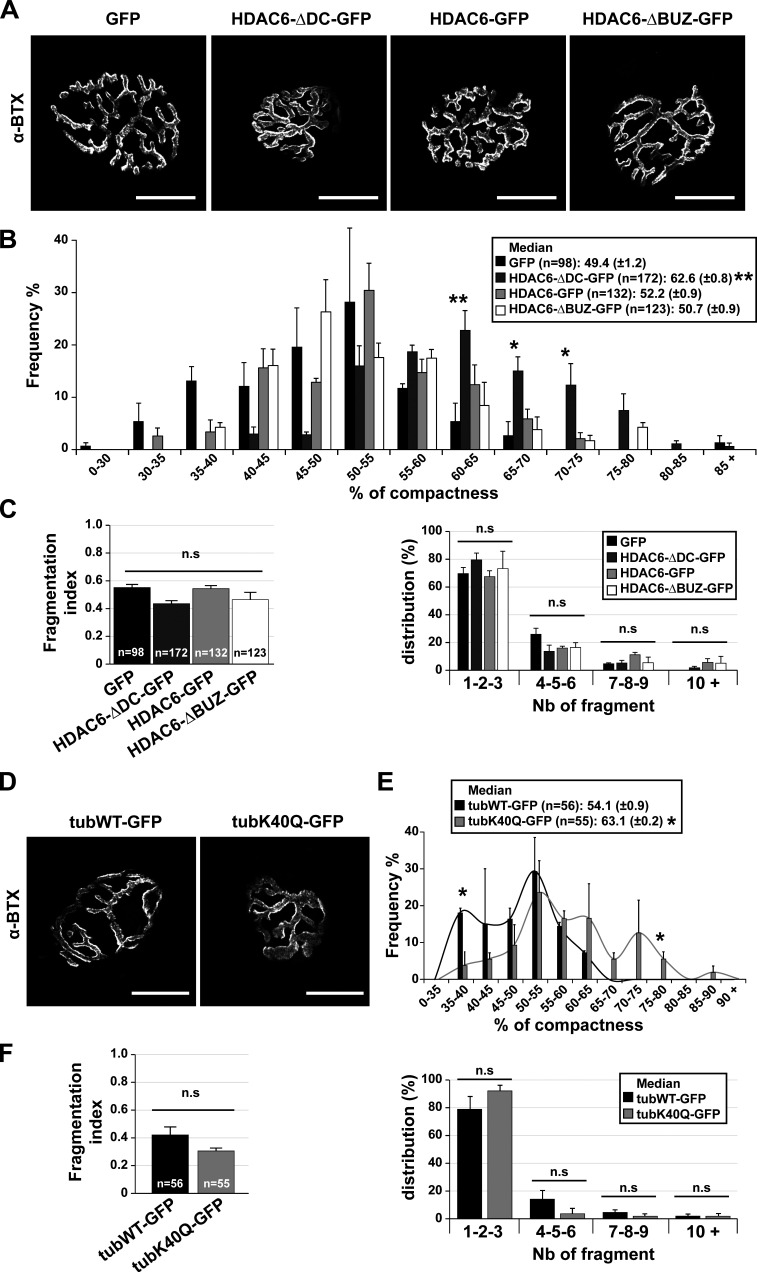
Figure 9.
In vivo, NMJ structure is regulated by HDAC6 inhibition via its catalytic domains and its interaction with lysine 40 of α-tubulin. (A and D) TA fibers were coelectroporated for 7 d with either one HDAC6 mutant (HDAC6-GFP; HDAC6-ΔDC-GFP; HDAC6-ΔBUZ-GFP) or a control GFP (A) or with WT tubulin (TubWT-GFP) or a mutant (TubK40Q-GFP; D). Myofibers were labeled with α-BTX–A594 (in gray), and only GFP-positive myofibers were selected. (B and E) Graphical summary of NMJ compactness (n = total number of NMJs, three to five mice for each condition; B and C between 98 and 172; E and F, TubWT-GFP = 56 and TubK40Q-GFP = 55). (C and F) Fragmentation index and distribution of number of fragments have been quantified (n = total number of NMJs counted on three to five mice for each condition). Graphs show means ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; n.s, not significant; Mann-Whitney U test. (A and D) Bars: 25 µm. n.s, not significant; Nb, number.