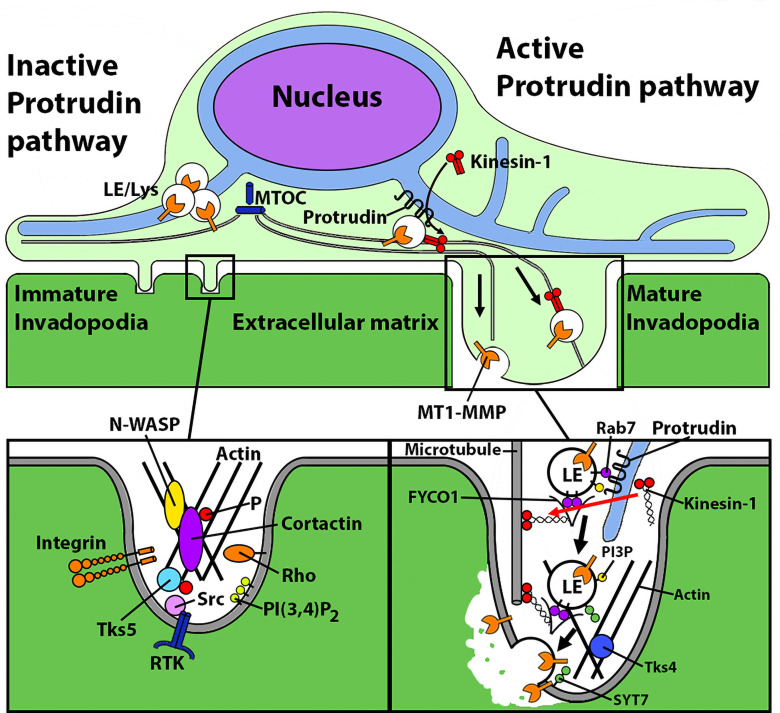
Figure 1.
Protrudin plays a dual role in invadopodia maturation. Schematic of Protrudin function as demonstrated in the study by Pedersen et al. (7). Left: Initiation of invadopodia formation, independent of Protrudin. Right: Invadopodia elongation and maturation, which require the Protrudin pathway. Protrudin promotes ER–endosome membrane contacts at which kinesin-1 is loaded onto FYCO1 on MT1-MMP-laden late endosomes (LE) to drive their anterograde transport and exocytosis, thus facilitating (a) invadopodia membrane extension and (b) ECM degradation/invasion. MTOC, microtubule-organizing center; P, phosphate; Tks5, tyrosine kinase substrate with 5 SH3 domains; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; SYT7, synaptotagmin 7.