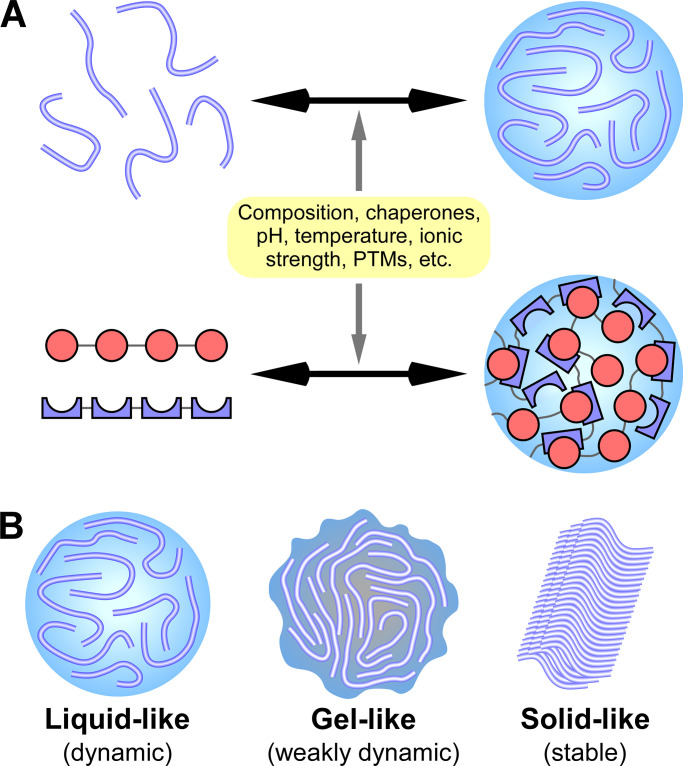
Figure 1.
Phase separation and transition mediate the assembly of protein condensates with distinct material properties. (A) Multivalent interactions, mediated by proteins containing IDRs (top) or tandem modular interacting domains (bottom, represented by the red circles and blue crescents in two different proteins), drive the formation of phase-separated liquid condensates. Factors affecting interactions, including composition, chaperones, pH, temperature, and various PTMs, modulate LLPS. (B) Liquid-like phase-separated condensates (with highly dynamic constituents) can transition into more stable states, such as the gel-like state (with less mobile constituents) and the inert solid state.