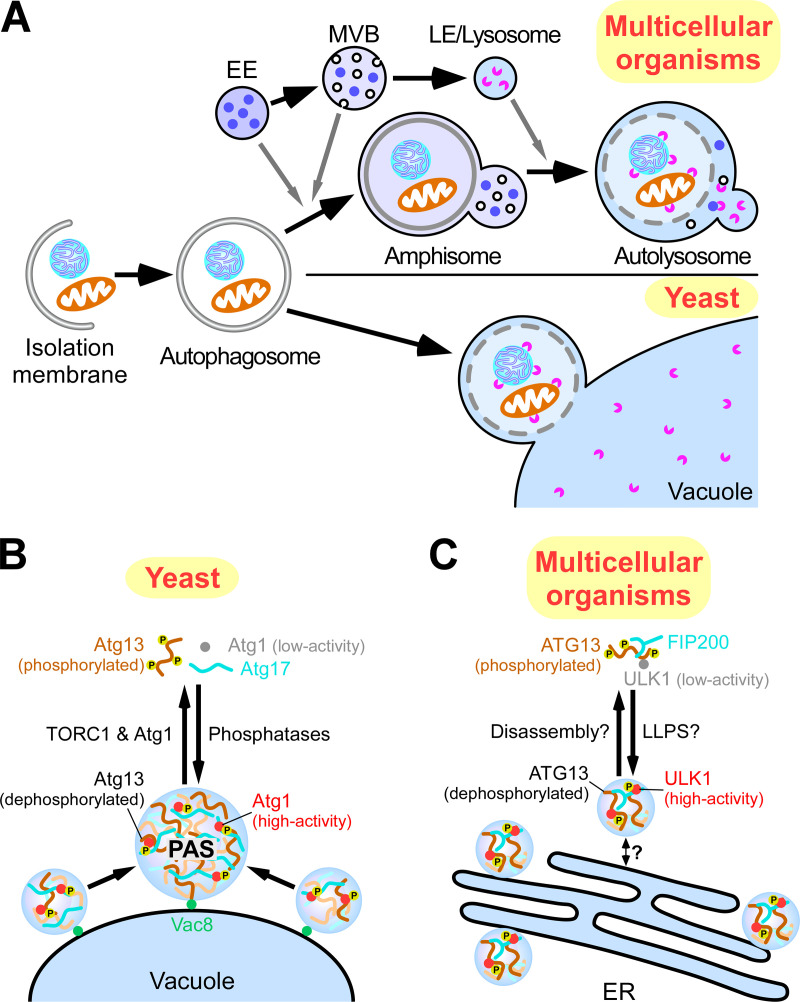
Figure 2.
Formation of autophagosomes in yeast and multicellular organisms. (A) Schematic illustration of the autophagy pathway in yeast and multicellular organisms. In multicellular organisms, closed autophagosomes undergo maturation by fusing with early endosomes (EEs) and/or multivesicular bodies (MVBs) to form amphisomes and with late endosomes/lysosomes (LE/lysosomes) to form autolysosomes. In yeast, autophagosomes directly fuse with the vacuole. (B) Organization of autophagosome formation sites by LLPS. In yeast, upon autophagy induction, Atg13 is dephosphorylated, and the ATG1 complex is formed, which undergoes LLPS to organize PAS precursors on the vacuolar membrane. PAS precursors coalescence into one PAS. (C) In mammals, upon autophagy induction, the ULK complex moves to the ER via an unknown mechanism and induces multiple autophagosome formation sites. This process might be caused by LLPS of the ULK complex.