Fig. 1.
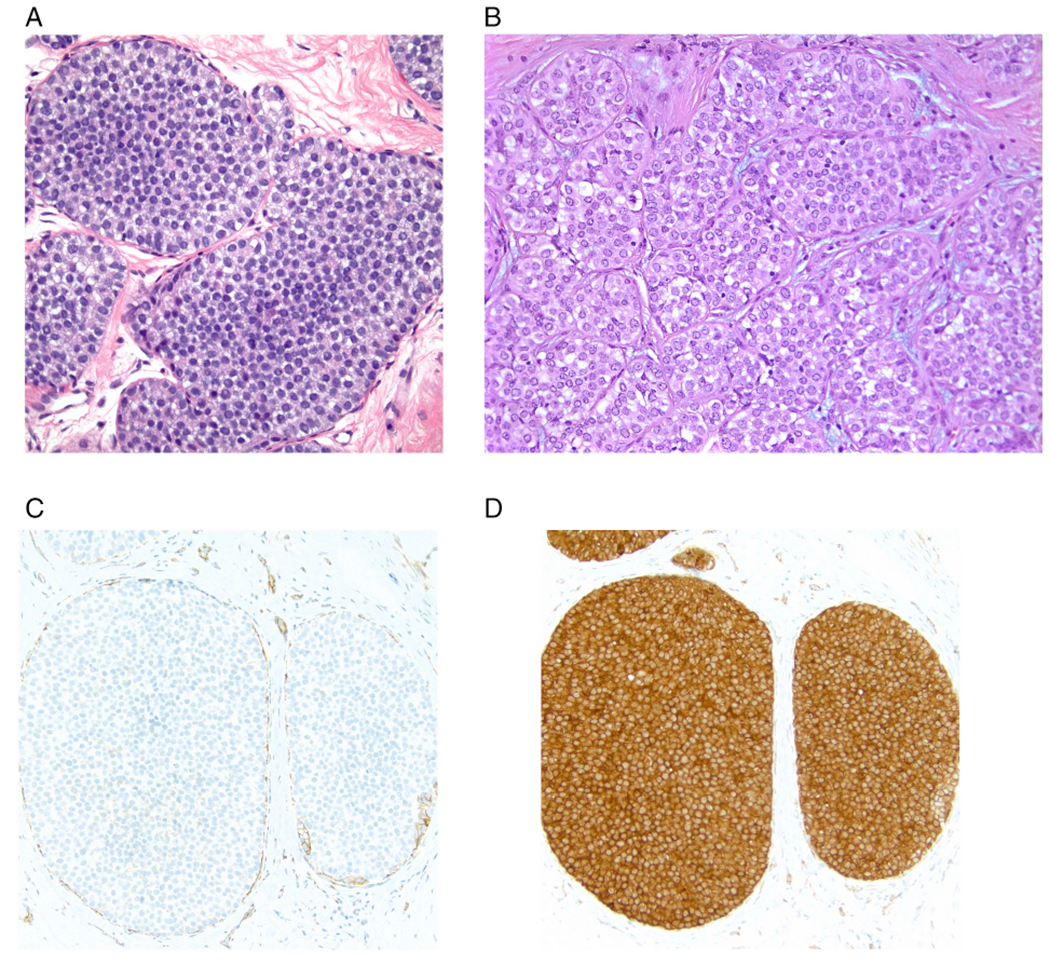
Classic lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). A. Type A cells. Small cells with uniform nuclei. B. Type B cells. The nuclei are larger and slightly more variable in size and shape than those seen in Type A cells. The chromatin is vesicular and small nucleoli are evident in some of the nuclei. C. E-cadherin immunostain demonstrating loss of membrane expression in the LCIS cells (note staining of surrounding myoepithelial cells). D. p120 catenin immunostain showing cytoplasmic staining of the LCIS cells.
