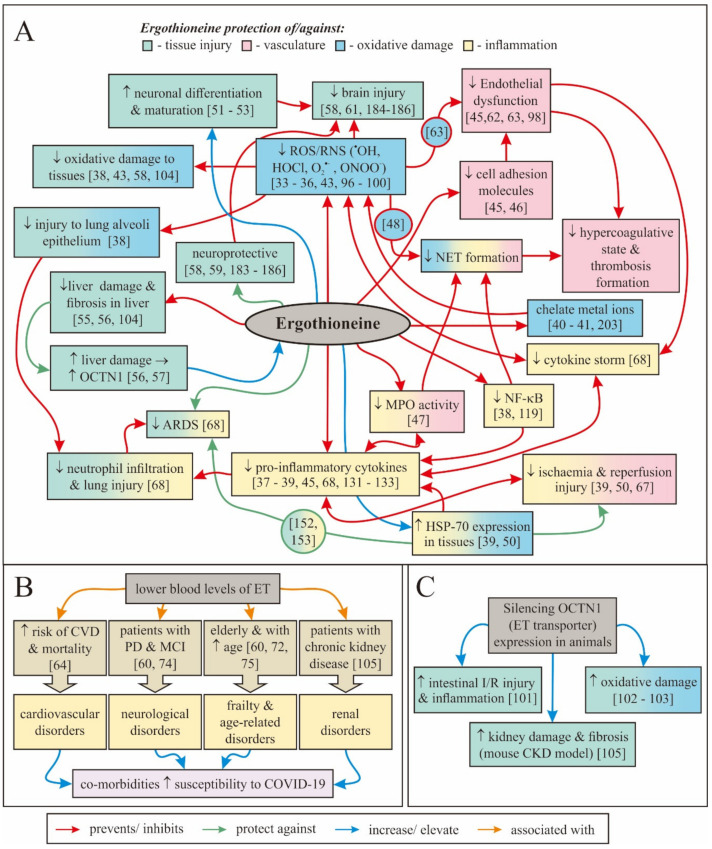
Figure 1.
Summary of possible mechanisms of action of ET: (A) An overview of the possible direct and indirect mechanisms by which ET can reduce the severity of symptoms in COVID-19 patients and thereby reduce mortality [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,43,45,46,47,48,50,51,52,53,55,56,57,58,61,62,63,68,96,97,98,99,100,104,119,131,132,133,152,153,184,185,186,203]. (B) Population studies have shown that lower blood levels of ET are associated with a wide range of disorders and frailty, suggesting that supplementation may assist or reduce the risk of these conditions. These disorders are also comorbidities that likely increase the risk of mortality due to COVID-19, possibly highlighting the greater therapeutic value of ET for these individuals [60,64,72,74,75,105]. (C) Conversely, silencing the ET transporter in animal studies increases susceptibility to diseases and may elevate oxidative damage and inflammation in these models [101,102,103,105].