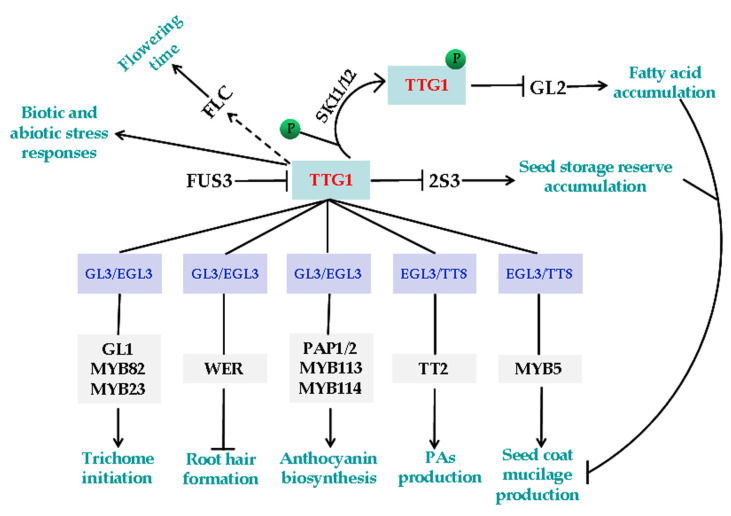
Figure 1.
The functions of TTG1. TTG1 regulates cell fate determination and secondary metabolism by forming MBW complexes with specific R2R3 MYB and bHLH transcription factors. The TTG1-GL3/EGL3-GL1/MYB23/MYB82 complexes regulate trichome initiation [25,30,60,61], the TTG1-GL3/EGL3-WER complexes regulate root hair formation [27,33], the TTG1-GL3/EGL3-PAP1/2/MYB113/114 complexes regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis [24,34,36], the TTG1-EGL3/TT8-TT2 complexes regulate proanthocyanidins (PAs) biosynthesis [24,28,34], and the TTG1-EGL3/TT8-MYB5 complexes regulate seed coat mucilage production [24]. TTG1 compromises the accumulation of seed storage reserves through inhibiting 2S3, and FUS3 can directly suppress the expression of TTG1. SK11/12 can phosphorylate TTG1, therefore inhibit GL2 expression, and affect fatty acid accumulation. TTG1 is also involved in regulating flowering, as well as biotic and abiotic stress responses.