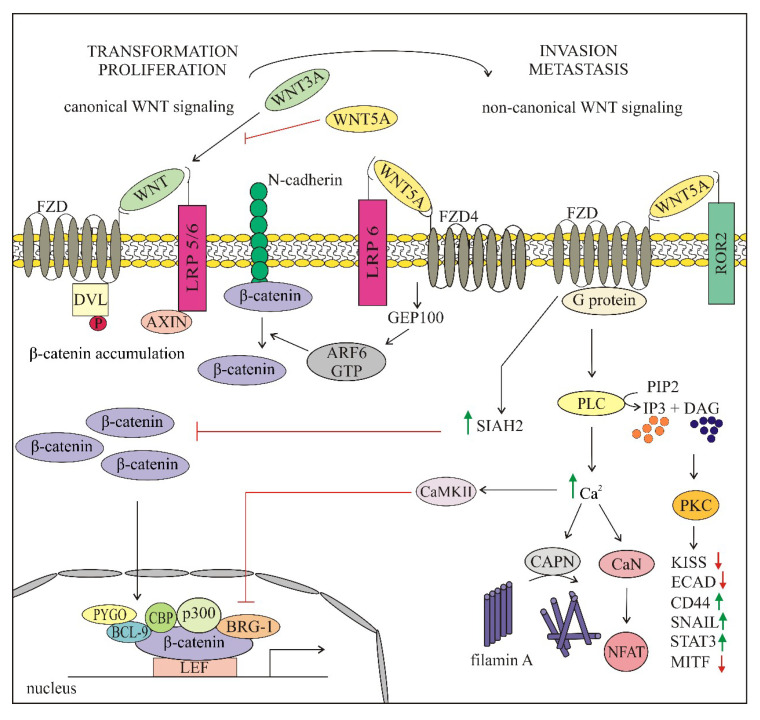
Figure 3.
Proposed model of the crosstalk between canonical and non-canonical WNT-signaling in melanoma. In the canonical WNT pathway, WNT–FZD/LRP5/6 interaction initiates β-catenin dependent signaling. β-catenin translocates to the nucleus to drive the transcription of target genes. This is critical for early steps of transformation when melanocytes bypass senescence and start to proliferate, thus promoting first the radial then vertical growth of melanoma. An increase of WNT5A that activates non-canonical WNT-signaling inhibits β-catenin-signaling and enhances the invasiveness of melanoma cells crucial for metastatic spreading of melanoma. Green and red arrows indicate increase and decrease, respectively.